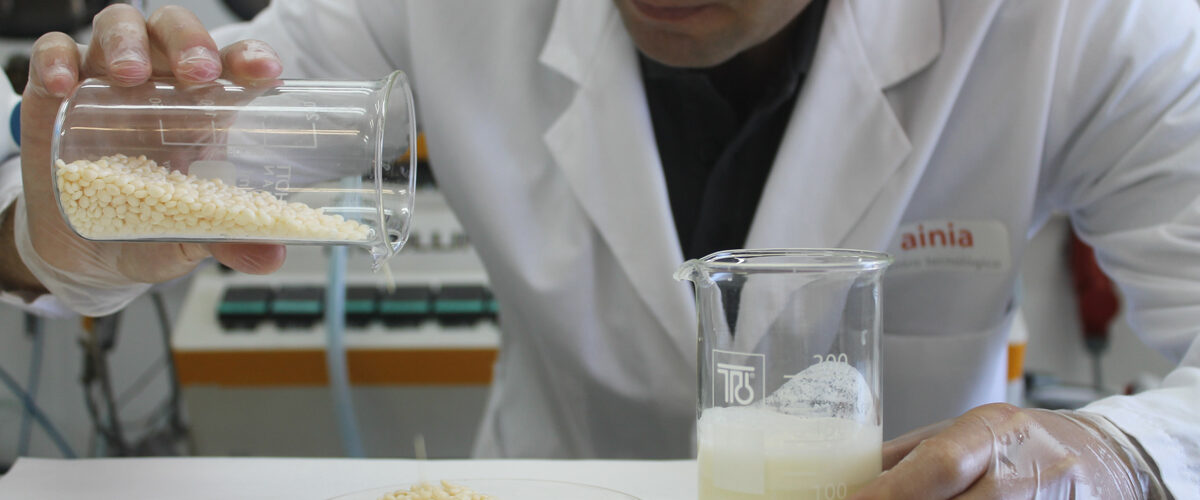
The Circular Lab has managed to create the first bioplastic that is made from plant waste and is biodegradable.
It is a multi-year initiative to raise awareness of the global plastic waste crisis.
Bioplastic simply refers to plastic made from plant or other biological material rather than petroleum. It is also often called bio-based plastic. They are, therefore, 100% degradable, just as resistant and versatile and are already used in sectors such as agriculture, the textile industry, medicine and above all, in the packaging and packaging market. Some advantages of bioplastics are: they reduce the carbon footprint.
Bioplastics are an alternative to reduce contamination by said synthetic plastics, since they are polymers that come from natural and renewable sources, they are all biodegradable by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi and algae.
We point out that a material, object or product is biodegradable when it can break down into the chemical elements that make it up, due to the action of biological agents and different types of environmental conditions. That is, when we talk about biodegradability, we are referring to the decomposition capacity of something. It is a natural process in which a material by biological action changes and generally loses its original properties and at a chemical level the molecules that make it up become simpler and more stable forms.
There are two types of biodegradation:
- Aerobic biodegradation, which occurs in the open air, where there is oxygen.
- Anaerobic biodegradation, which takes place in the absence of this compound.
Biodegradable materials are:
- Fruit and vegetable remains: Vegetables, shells, eggshells, grains, remains of prepared food.
- Lawn and garden pruning waste: Grass, branches, leaf litter, green crop residues.
- PLA (polylactic acid). Derived from lactic acid made with 100% renewable raw materials.
- PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates). From the bacterial fermentation of vegetable raw materials.
- Starch-based bioplastics.
- Bioplastics based on cellulose.
Sawdust is ideal to add to plant fertilizer. Dry leaves of the trees; they degrade in a short time and work on their own as soil fertilizers.
The Branches: Like wood, they are biodegradable and work for some crafts or home decorations.
Biodegradable products begin to degrade after around 18 months (which is why they have a manufacturing date) up to a period of between 1 and a half to 3 years, which is actually not a short time.
Biodegradable products can help improve the environment because they do not pollute the soil and water, because they disappear quickly and do not leave toxic residues, they do not saturate landfills, they serve as food for the planet, and they can be cheaper.
The decomposition process of biodegradable plastics is much faster than that of conventional plastic resins.
Plastics are classified for recycling as follows:
As there is a great diversity of plastic materials, the typology to identify them is varied. If the acronym has an “R” (example R-PET), it means that the product contains recycled plastic.
Conventional plastics are not biodegradable, that is, they do not serve as food for any living being. According to the Ecologists in Action report, getting rid of plastic only degrades with solar radiation, losing resistance and breaking into smaller and smaller particles, without changing its chemical composition.
A large percentage of the plastic that is not recycled ends up in our oceans; that is, to the habitat and organism of the 100,000 marine mammals that die each year from this pollution.
Definition:
Biodegradable plastic: Biodegradable plastics under certain temperature and humidity conditions are consumed by microorganisms and enter into an oxidation process that favors their conversion into water, carbon dioxide and biomass. In this way, they are reintegrated into the carbon cycle without leaving residues.
https://www.rajapack.es/blog-es/tipos-plasticos-biodegradables