Transgenic Organisms. Advantages, Disadvantages and their Importance in Human Health.
Transgenic organisms are generated in the laboratory for research purposes.
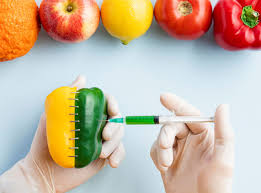
Transgenic represents an organism or cell whose genome has been altered by the introduction by artificial means of one or more sequences of foreign DNA from another species.
The main objective of these transgenic organisms is to provide these cells with special qualities that they would lack. So transgenic plants can survive pests, withstand droughts better, or resist the effect of some herbicides. The UN defends genetically modified crops as a weapon against hunger. Transgenic foods can be key to reducing hunger and malnutrition that affect millions of people.
A transgenic is a living being artificially created through a technique that allows genes from viruses, bacteria, plants, animals and even humans to be inserted into a plant.
Advantages:
Some of the scientific studies currently suggest that genetically modified foods do not pose a risk to human health, have shown that they are approved for consumption and are as safe as their non-genetically modified counterparts.
Likewise, they can contribute to guaranteeing greater availability of food and significant economic benefits for the agricultural production sector.
Disadvantages:
Transgenic foods could be harmful to human health. However, there is no scientific approval in this regard.
For this reason, it is believed that they can cause the following long-term effects or diseases on human health: appearance of new allergies due to the introduction of new proteins in food, resistance to antibiotics in pathogenic bacteria, fertility problems, affectation of the immune and hormonal systems and various internal organs.
It is important to know that the first genetically modified or transgenic food was created in 1994, the FlavrSavr tomato, so that it would have a longer shelf life.
Likewise, it is important to know that the first genetically modified or transgenic animal was a mouse, in 1980. Two years later, researchers introduced the rat growth hormone gene into mice.
There are three types of transgenic organisms produced today:
- Transgenic microorganisms: yeasts, fungi and bacteria, used to obtain medical and food substances.
- Transgenic plants, for example, have had their genes altered to make them resistant to certain pests, to intensify crop production.
- Transgenic animals: In genetically modified animals, the inserted genes may not function as intended, often resulting in anatomical, physiological and behavioral abnormalities.
The most common genetically modified foods are: soybeans, corn, cotton, canola, sugar beets and herbicide-tolerant alfalfa; insect-resistant corn, cotton, eggplant and sugarcane (Bt); corn, cotton and soybeans with tolerance to herbicides.
Their importance lies in the fact that they are more nutritious, tastier foods, plants that are more resistant to drought and diseases and could become a tool against hunger.
FONT
https://www.diferenciador.com/ventajas-y-desventajas-de-los-alimentos-transgenicos/
YOU MAY ALSO BE INTERESTED
Stem Cells generate new neuronal connections
https://www.medicalpharmanews.com/en/stem-cells-generate-new-neuronal-connections/