Nanotechnology is the science involved in the design of functional materials, devices and systems through the control of matter at the nanometric scale, dimensions in which the physical, chemical and biological properties of materials change radically, which allows interaction with cellular and molecular level with a high degree of specificity.
Nanomedicine is the application of nanotechnology to medicine in order to exert control over biological structures, with molecular and atomic precision, in order to maintain and establish health
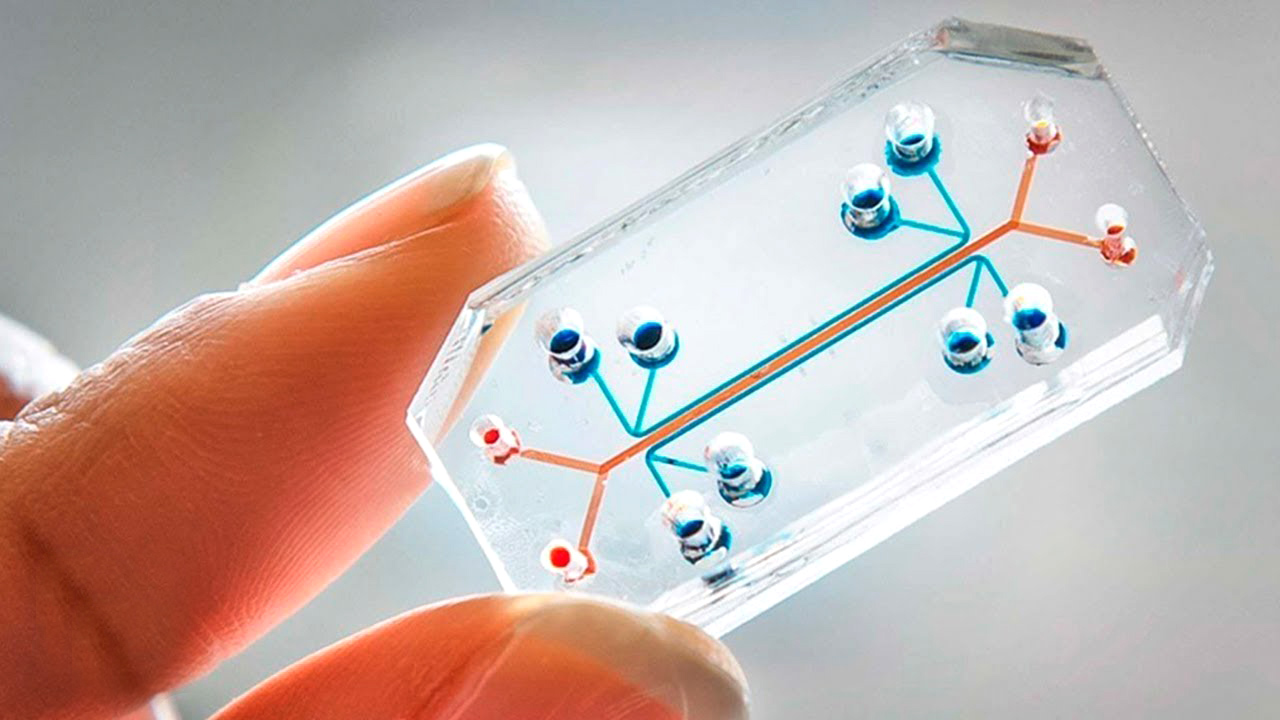
Applying scientific advances and nanotechnology would move medical laboratories within a small chip, which would be of great advantage, because in the short term we would be talking about detecting diseases in time, although some are in our body and are very difficult to discover by not show symptom, it would also help to apply treatments or for possible healing. This chip could be incorporated into a portable device and send the information to the cloud. This, relating it with data from other devices, could provide a complete map of our health and quickly alert us to the first symptom.
The laboratories will have to link their labors with other much more sophisticated centers that will allow to know the details of the conventional parameters and the most novel ones.
Currently, areas for study have been promoted, such as Bioelectronics and Nanoscience, whose main objective is research in systems with application in biomedicine. Another area is the design of biomolecular detectors (biosensors) for the personalized detection of DNA or its modification. Cellular bioengineering is another branch where nanotechnologies also allow the development of clinical applications.
These and other innovations are now possible in Pharmamedic.