[et_pb_section bb_built=”1″][et_pb_row][et_pb_column type=”4_4″][et_pb_text _builder_version=”3.13.1″]
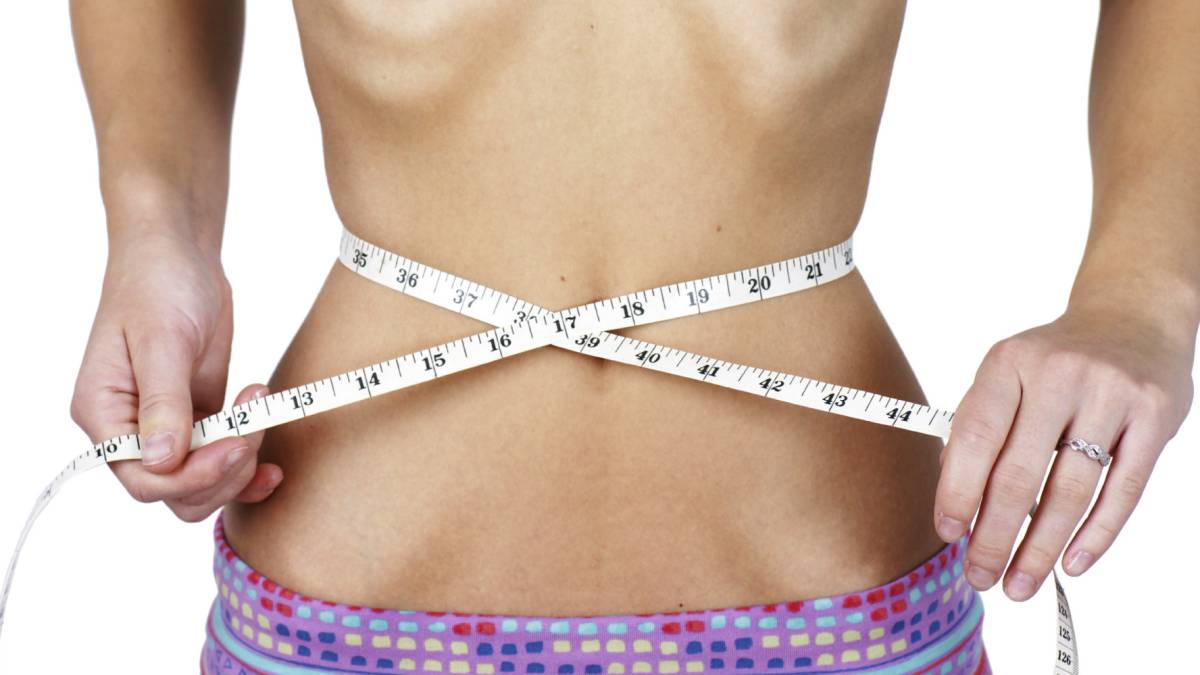
Anorexia nervosa is a group of severe eating disorders that include periods of food deprivation (anorexia), alternated occasionally with compulsive periods of food intake and purge (bulimia), both periods associated with other behavior disorders food not specified.
This pathology is very rare before puberty and usually affects a greater percentage of girls, although each time the age of appearance is advancing more and equating the percentage of cases between both sexes. On average, anorexia nervosa is considered to appear around 17 years of age. The earlier the age of onset and the earlier its detection and treatment, the better the cure prognosis.
In all cases, patients are not usually able to recognize their problem of extreme thinness, given that they are not aware of their condition, categorically denying their condition, and even isolating themselves from nearby people because they believe they want to make them “fatter more” , and that the problem of vision of reality has its environment and not them.
There are certain signs and symptoms that make you suspect that a person may be suffering from anorexia nervosa, however, the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up should always be performed by a specialist health professional. These signs are:
- Excessive weight loss in a short space of time.
- Constant feeling of unfounded obesity and iron desire to keep losing weight, with active control (look repeatedly in the mirror, weigh yourself several times a day, count calories …).
- Delay in growth and development (in children and adolescents).
- Alterations of menstruation or absence of it.
- Realization of constant and excessive physical exercise.
- Run away from the table after eating.
- Disguise the food so as not to ingest it (split into small pieces and spread it over the plate, throw it on the floor, hide it …).
- Progressive isolation and loss of social ties.
- Altered mood with tendency to depression and anxiety.
- Obsession with the caloric content of everything that is consumed, taking only low-calorie foods.
Some symptoms of anorexia:
In the clinical setting, the main symptoms of anorexia nervosa are:
- Dry skin, with the possibility of cracks.
- Appearance of fine hair (lanugo) on cheeks, back, thighs and forearms.
- Yellowish pigmentation on the skin, mainly on the soles of the feet and the palms of the hands. This is due to an increase in blood carotenoids (precursors of vitamin A) due to a disorder in their metabolism.
- Cold limbs.
- Brittle nails and hair loss.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: flatulence, bloating, abdominal pain and constipation (except if laxatives are used that can cause diarrhea that alter the electrolyte balance).
- Cardiovascular disorders: low blood pressure (hypotension), decreased heart rate (bradycardia), heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias), and so on.
- Hemogram: low levels of red blood cells (anemia) and white blood cells (leukopenia).
The diagnosis of anorexia is based on the following key aspects:
- An interview with the patient and their closest family environment, and review of their medical history and family history.
- A physical examination and evaluation of heart rate, blood pressure and respiratory rate.
- Complementary clinical tests: blood count, biochemistry, etcetera.
Always take care of your health with a unique and efficient service. Visit Pharmamedic.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]