La sciatica è chiamata irritazione del nervo sciatico che induce il paziente a sentire dolore nella parte bassa della schiena, un dolore che si estende alla parte posteriore di una delle gambe, e può talvolta raggiungere la punta del piede . A volte il nervo irritato non è esattamente il nervo sciatico, e il dolore colpisce la parte laterale o anteriore della gamba, ma di solito è mantenuto il nome di attacco di sciatica o sciatica in lingua popolare.
La sciatica, che si verifica a causa di irritazione del nervo sciatico, è molto dolorosa e può durare diversi giorni, eventualmente invalidando il paziente. È una delle cause più frequenti di consulenza medica e assenze per malattia tra gli uomini di mezza età.
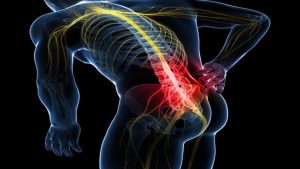
Le radici di questo nervo derivano dal midollo spinale, escono attraverso le vertebre e si fondono per formare il nervo, che è largo quanto un dito della mano (è il più grande nervo del corpo umano). Da lì scende alla gamba dietro le natiche, la coscia e il ginocchio, innervando tutti i muscoli che trova sul percorso e la pelle del suo percorso fino a raggiungere il bordo esterno del piede.
Le cause più frequenti di sciatica sono: ernia del disco vertebrale, stenosi del canale lombare, sindrome di Piriforme, fratture, tumori, morbo di Paget, gravidanza.
Il sintomo principale dell’attacco di sciatica è il dolore, sebbene il dolore possa variare notevolmente in intensità e caratteristiche. Può essere causato da un dolore sordo che dura diversi giorni, da un dolore che appare quasi improvvisamente e con grande intensità e impedisce al paziente di spostarsi dalla sedia. In ogni caso, il dolore colpisce sempre uno dei lati, dai glutei al ginocchio, i polpacci o anche il piede. È anche frequente essere accompagnati da dolore nella parte bassa della schiena, motivo per cui i medici la chiamano lombociatalgia. Il dolore può aumentare con il movimento (alzarsi, sedersi) o con una maggiore pressione all’interno dell’addome (tossire, defecare). Può anche apparire prima di coricarsi o quando ti svegli al mattino sdraiato sul letto, ma di solito non interrompe il sonno nel cuore della notte.
Altri sintomi frequenti sarebbero la debolezza muscolare e la diminuzione dei riflessi muscolari. Il nervo sciatico, essendo danneggiato, non può innervare correttamente i muscoli e i movimenti dell’anca e del ginocchio sono limitati. Ecco perché le persone con la sciatica camminano zoppicando o non possono alzarsi dal letto da sole.
Il riposo relativo, cioè, il paziente sarà in grado di muoversi, ma non dovrebbe fare sforzi o camminare per lunghe distanze. Il riposo a letto non è raccomandato una volta che il dolore è alleviato con analgesici.
Corticosteroidi: devono essere somministrati solo in situazioni in cui gli antinfiammatori non sono sufficienti.
Applicare freddo nella zona lombare o nei glutei ha interessato i primi due giorni di dolore. Ciò ridurrà l’infiammazione che accompagna la compressione del nervo. Il freddo verrà applicato per 10-15 minuti e sempre indirettamente, coprendo il ghiaccio con panni.
Applicare calore nei giorni seguenti con una coperta elettrica, una bottiglia di acqua calda o un bagno. Non superare i 20-25 minuti di applicazione. Calma il dolore ed è più efficace quando il dolore è accompagnato da contratture muscolari.
Massaggi nella zona lombare; hanno lo stesso effetto dell’applicazione del calore. Devono essere fatti da persone addestrate.
Ci sono segnali di pericolo che costringono il medico a eseguire più test per escludere tumori, lesioni ai nervi o altre gravi cause di sciatica. Questi segni sono:
- Avere più di 50 anni e non aver subito precedenti attacchi di sciatica.
- Non rispondere al trattamento dopo quattro settimane.
- Aumento progressivo dell’area senza sensibilità.
- Perdita di controllo dell’intestino o della vescica.
- Perdita di peso o di appetito o febbre accompagnatoria.
- Cancro precedente.
- Endocardite o sepsi precedente.
In presenza di uno qualsiasi di questi segni, è necessario eseguire un esame del sangue, una radiografia della colonna vertebrale e una risonanza magnetica.
Per prevenire la sciatica, le migliori misure che possono essere prese sono:
- Evitare l’obesità e il sovrappeso.
- Cammina un minimo di cinque ore a settimana.
- Praticare sport che favoriscono lo sviluppo dei muscoli lombari, come il nuoto o il tennis. Lo yoga può anche aiutare a mantenere un buon tono muscolare.
- Non piegarti con la schiena, ma piega le ginocchia con la schiena dritta.
- Non caricare pesi pesanti.
- Non adottare cattive posizioni seduti alla scrivania o guidando. La parte bassa della schiena deve essere sempre supportata sullo schienale o su un cuscino.
- Dormire su materassi flessibili ma rigidi, in modo che la colonna sia sempre in posizione diritta.
Prenditi sempre cura della tua salute con un servizio unico ed efficiente. Visita Pharmamedic.






