Strengthening Your Natural Shield: A Comprehensive and Extended Guide to the Immune System.
The immune system is produced in the bone marrow, which is found primarily within the long bones, vertebrae, and pelvic bones of the body. Thus, the marrow produces white blood cells that destroy bacteria, viruses, and other organisms that cause infections.
Our immune system is a marvel of biology, an intricate network of cells, tissues, and organs designed to defend us against a universe of invisible threats.
From bacteria and viruses to fungi and parasites, our immune system works tirelessly, 24/7, to keep us healthy. Therefore, understanding how it works and how we can strengthen it is critical to enjoying a full and active life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore in-depth natural strategies, the role of supplements, the importance of healthy habits, and the power of key foods to optimize our immune system function.
Do you know why your immune system weakens?
An immune system can weaken for several reasons:
- Poor diet.
- Frequent temperature changes.
- Suffering from illnesses such as anemia.
- Exposure to pollutants.
The Immune System: A Complex Internal Army
Before delving into how to strengthen it, it’s essential to understand the key components of the immune system. This system is not a single organ, but rather a collection of elements that include:
- Leukocytes (white blood cells): These are the first-line defense cells, responsible for identifying and eliminating pathogens. They are divided into several types, each with a specific function:
o Lymphocytes: These include B cells (which produce antibodies) and T cells (which destroy infected cells).
o Phagocytes: Such as macrophages and neutrophils, which “eat” invaders and cellular debris.
- Antibodies: Proteins produced by B cells that attach to pathogens, marking them for destruction by other immune cells.
- Complement system: A group of proteins that work together with antibodies to destroy pathogens and promote inflammation.
- Lymphoid organs: These include the bone marrow (where immune cells are produced), the thymus (where T cells mature), the spleen (which filters the blood and stores immune cells), and the lymph nodes (which house immune cells and filter lymphatic fluid).
- Physical barriers: The skin, mucous membranes, and stomach acid act as the first line of defense, preventing pathogens from entering the body.
Nutrition: The Essential Fuel for a Robust Immune System
Proper nutrition is, without a doubt, the cornerstone of a strong immune system. The nutrients we get from food are the building blocks and fuel our immune cells need to function optimally.
A balanced diet, rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, provides the necessary support for our immune system to effectively fight infections and keep us healthy.
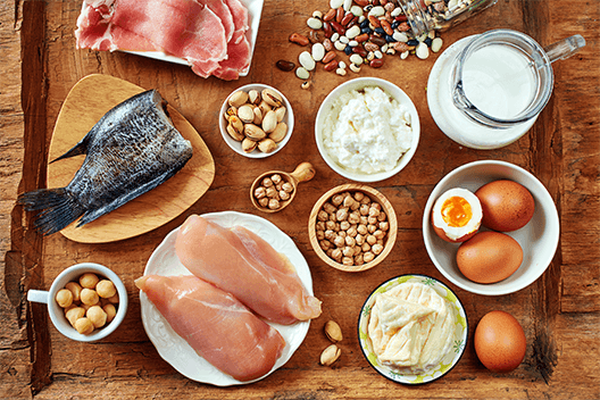
Key Foods to Strengthen Your Immune System:
- Colorful Fruits and Vegetables: These foods are true nutritional powerhouses, packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
o Vitamin C: Found in abundance in citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruit, as well as strawberries, kiwis, peppers, and broccoli. Vitamin C is a key antioxidant that helps protect immune cells from damage and stimulates the production of white blood cells.
o Vitamin A: Found in foods such as carrots, sweet potatoes, squash, spinach, and other leafy greens. Vitamin A is essential for maintaining the integrity of mucous membranes, which act as barriers to prevent the entry of pathogens.
- Antioxidants: Brightly colored fruits and vegetables (berries, purple grapes, beets), dark chocolate (in moderation), green tea. Blueberries, raspberries, and pomegranates are rich in antioxidants such as anthocyanins, which combat oxidative stress and protect immune cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Garlic and onion: More than just a condiment: These spicy foods contain sulfur compounds, such as allicin in garlic, which have been shown to have potent antimicrobial, antiviral, and antifungal properties.
Additionally, they can stimulate the activity of certain immune cells, such as natural killer cells, which play a crucial role in eliminating infected cells.
- Ginger: An ally against inflammation: This spicy root is known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Ginger can help relieve symptoms of colds and flu, such as sore throat and congestion, while supporting the immune response by modulating the production of cytokines, molecules that regulate inflammation.
- Turmeric: The power of curcumin: This golden spice contains curcumin, a compound with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Curcumin has been shown to modulate the immune response by influencing the activity of various immune cells and suppressing the production of pro-inflammatory molecules.
- Yogurt and fermented foods: The secret is in the gut: These foods are rich in probiotics, beneficial bacteria that promote a healthy gut microbiome.
Since a large part of our immune system resides in the gut, maintaining a healthy balance of gut bacteria is vital for an optimal immune response. Probiotics help strengthen the intestinal barrier, preventing the entry of pathogens, and can also stimulate the production of immune cells and antibodies. Examples of fermented foods include kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha.
- Mushrooms: A natural boost: Some mushroom varieties, such as shiitake, maitake, and reishi, contain beta-glucans, compounds that have been shown to have immunomodulatory properties.
Beta-glucans can stimulate the activity of immune cells, such as macrophages and natural killer cells, improving their ability to fight infections.
- Seeds and nuts: Small but mighty: They are an excellent source of vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that supports immune function by protecting cells from oxidative damage.
They are also rich in other essential nutrients such as zinc, selenium, and magnesium, which play an important role in regulating the immune response. Sunflower seeds, almonds, Brazil nuts, and chia seeds are excellent options.
Supplements: Cautious Additional Support for Your Immune System
In an ideal world, a balanced diet would provide us with all the nutrients we need for a healthy immune system. However, in certain situations, such as during periods of stress, illness, or nutritional deficiency, supplements can offer additional support.
However, it is crucial to approach supplementation with caution and always under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Supplements that may support your immune system:
- Vitamin C: A classic antioxidant: Vitamin C is a well-known antioxidant that plays a crucial role in several immune functions. It helps stimulate white blood cell production, protects immune cells from damage, and is involved in antibody production.
While evidence regarding its ability to prevent the common cold is mixed, some studies suggest that vitamin C supplementation may reduce the duration and severity of symptoms in some people.
Example: Citrus fruits (orange, lemon, tangerine, grapefruit), kiwi, strawberries, peppers, broccoli, tomato.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a vital role in regulating the immune system.
It helps modulate the immune response, promoting the production of antimicrobial peptides and regulating the activity of T and B cells. Vitamin D deficiency has been associated with an increased risk of respiratory infections and other diseases.
Sun exposure is one of the main ways our bodies produce vitamin D, but supplementation may be necessary, especially for people with limited sun exposure or in regions with little sunlight.
Example: Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel), egg yolk, fortified dairy products.
- Zinc: An essential mineral: Zinc is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in the development and function of immune cells. Zinc is involved in the activity of almost all cells in the immune system, including T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells.
Zinc deficiency can weaken the immune response, increasing susceptibility to infections. Some studies suggest that zinc supplements may reduce the duration and severity of the common cold if taken at the onset of symptoms, but more research is needed to confirm these findings.
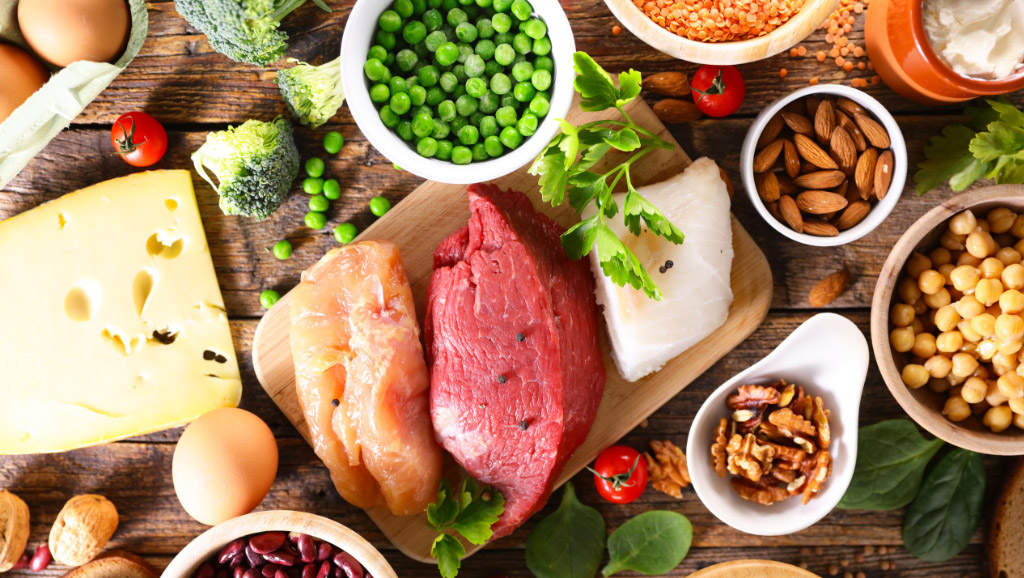
Examples: Oysters, lean red meat, chicken, legumes, nuts, seeds.
- Probiotics: Balance is key: As mentioned above, a healthy gut microbiome is critical for an optimal immune response.
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer health benefits to the host.
They help maintain or restore the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut, strengthening the intestinal barrier, preventing the proliferation of pathogens, and modulating the immune response.
Examples: Plain yogurt with live cultures, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi.
Probiotic supplements may be beneficial for people with imbalances in their gut microbiome or to support overall immune health.
- Echinacea: A Traditional Herb: Echinacea is a popular herb that has been traditionally used to treat colds and other respiratory infections.
Some studies suggest that echinacea may help boost the immune system by increasing the activity of certain immune cells, such as macrophages.
However, evidence regarding its effectiveness is mixed, and more research is needed to determine its role in preventing and treating infections. • Elderberry: An ally against viruses: Elderberry extracts have been shown to have antiviral properties, especially against the influenza virus.
They can help reduce the duration and severity of flu symptoms by inhibiting viral replication and stimulating the immune response.
- Selenium: A protective antioxidant: Selenium is an essential mineral that acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals.
It also plays a crucial role in immune function, participating in the activity of several immune enzymes and proteins. Selenium deficiency can negatively affect the immune response, increasing susceptibility to infections.
Examples: Brazil nuts, tuna, sardines, chicken, eggs.
Other supplements that can help boost your immune system include:
- Vitamin E: Almonds, walnuts, sunflower seeds, avocado.
- Prebiotics: Garlic, onion, leek, asparagus, oats, banana.
- Lean proteins: Chicken, turkey, fish, legumes, tofu.
- Healthy fats: Extra virgin olive oil, avocado, nuts, seeds.
It is important to emphasize that supplements are not a magic bullet and cannot replace a healthy diet and a balanced lifestyle.
The effectiveness of supplements may vary among individuals, and the dosage and duration of treatment should be individualized and supervised by a healthcare professional. Additionally, some supplements may interact with medications, so it is essential to inform your doctor about any supplements you are taking.
Healthy Habits: The Foundation of a Strong and Resilient Immune System
Beyond nutrition and supplementation, our daily habits play a fundamental role in determining the strength of our immune system.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is one of the most valuable investments we can make in our long-term health.
Key Habits to Strengthen Your Immune System:
- Adequate Rest: The Restorative Power of Sleep: Getting 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep each night is essential for cell regeneration, tissue repair, and optimal immune function.
During sleep, our bodies produce and release cytokines, proteins that play a crucial role in regulating inflammation and immune response. Chronic sleep deprivation can suppress immune function, increasing susceptibility to infections and other illnesses. Prioritizing quality sleep is just as important as a healthy diet and regular exercise.
- Stress Management: The Silent Enemy of Immunity: Chronic stress can have a devastating impact on our immune system.
When we are stressed, our bodies release hormones like cortisol, which can suppress immune function by inhibiting immune cell activity and reducing antibody production.
Implementing effective stress management techniques is crucial to protecting our immune health. Some helpful strategies include meditation, yoga, regular exercise, deep breathing, spending time in nature, practicing relaxing hobbies, and seeking support from friends and family.
- Regular exercise: Move to stay healthy: Regular physical activity, especially moderate exercise, offers numerous benefits for immune health.
Exercise improves blood circulation, allowing immune cells to move through the body more efficiently, detecting and eliminating pathogens.
It also helps reduce stress, promotes healthy sleep, and may improve immune cell function. However, strenuous or prolonged exercise can have a temporary suppressive effect on the immune system, so moderation and balance are key.
- Proper Hygiene: Prevention is the best medicine: Maintaining good hygiene is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of infections.
Washing your hands frequently and properly, especially after using the bathroom, before eating, after blowing your nose, coughing, or sneezing, and after being in public places, can significantly reduce the risk of contracting and transmitting diseases.
In addition to handwashing, covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, avoiding touching your face, and cleaning and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces are also important practices.
- Avoiding tobacco use and limiting alcohol: A blow to your defenses: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on the immune system. Smoking damages the respiratory system, making it difficult for the body to fight lung infections, and also suppresses immune cell function. Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with white blood cell production and weaken the immune response. Quitting tobacco and limiting alcohol consumption is critical to maintaining a healthy immune system.
- Staying hydrated: The elixir of life and immunity: Drinking enough water is essential for overall health and also plays an important role in supporting the immune system.
Water helps transport immune cells through the bloodstream, allowing them to reach where they are needed. It also helps remove toxins and waste products from the body, which is important for optimal immune function.
The amount of water each person needs varies, but a good rule of thumb is to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day.
- Moderate sun exposure: Balance is key: Sun exposure helps our bodies produce vitamin D, which, as mentioned above, is crucial for immune function. However, it is important to balance the benefits of sun exposure with the risks of skin damage and skin cancer. Moderate sun exposure, generally 10 to 15 minutes a day, several times a week, may be enough to stimulate vitamin D production without significantly increasing the risk of skin damage.
Using sunscreen is important to protect the skin from the harmful effects of prolonged sun exposure.
Boost Your Immune System with This Menu.
Below is a daily menu for better health and well-being.
Breakfast:
- Fresh orange juice or a smoothie with fruit (strawberries, banana, kiwi) and yogurt.
- Whole-wheat toast with avocado and an egg.
- Oatmeal with berries and nuts.
Mid-morning snack:
- A piece of fruit (apple, orange, pear).
- A handful of almonds or walnuts.
Lunch:
- Large, varied salad with green leaves, tomato, grated carrot, bell pepper, avocado, and grilled chicken or tuna. Dress with olive oil and lemon.
- Lentil soup with vegetables (carrot, onion, celery).
- Baked salmon with asparagus.
Mid-afternoon:
- Natural yogurt with fruit.
- A handful of sunflower or pumpkin seeds.
Dinner:
- Homemade vegetable soup (pumpkin, carrot, broccoli).
- Spinach and onion omelet.
- Steamed white fish with salad.
It’s important to use herbs and spices: Incorporate garlic, ginger, turmeric, and onion into your dishes, as they have beneficial properties for immunity.
Similarly, green juices are recommended for their antioxidant, diuretic, and anti-inflammatory properties, and they also help strengthen your body’s defenses.
Integrating Strategies for Optimal and Long-Lasting Immunity
In summary, the immune system is made up of organs and tissues, including the bone marrow, spleen, thymus, tonsils, mucous membranes, and skin. Granulocytes, macrophages, and T lymphocytes are examples of specialized cells.
It is important to know that HIV gradually destroys the immune system.
Strengthening the immune system naturally is a multifaceted process that requires a holistic approach. It involves nourishing our bodies with a diet rich in key foods, considering the strategic use of supplements, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and understanding the intricate web of factors that influence our immune response.
By integrating these strategies into our daily lives, we can build a stronger and more resilient protective shield, not only to fight off disease but also to promote optimal health and well-being throughout our lives. A strong immune system not only protects us from infectious diseases but also plays a crucial role in preventing chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and some types of cancer.
Therefore, investing in our immune health is an investment in our overall health and quality of life.
We invite you to read another interesting article:
Gene Therapy: 1 Great Power of DNA. Heal!
Font:
IA: Queries in scientific and medical literature.