The history of surgical robots is considered to begin in 1985 with the PUMA 560 robot, an industrial robotic arm used to try to increase the precision in performing brain biopsies by puncture.
The world’s first robot surgeon was “Arthrobot”, developed and first used in Vancouver, Canada in 1983. The robot was developed by a team led by Dr. James McEwen and GeofAuchinlek, working in collaboration with orthopedic surgeon Dr. Brian Day.
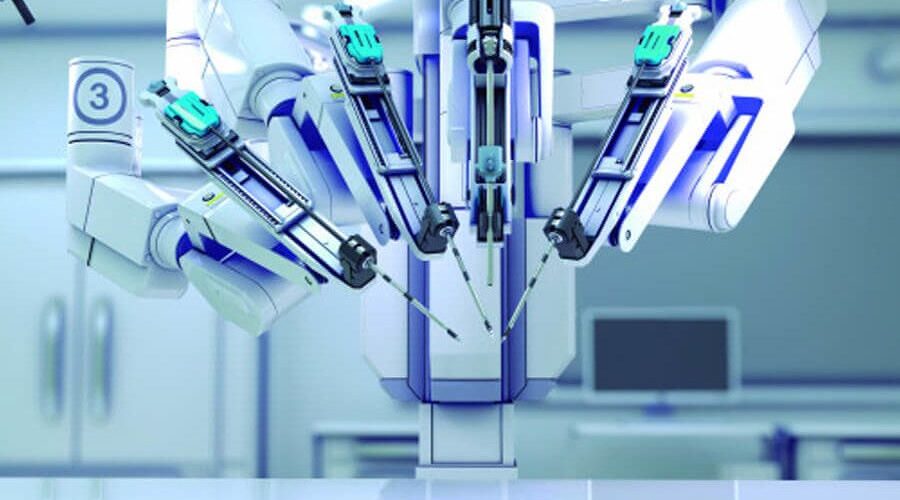
It is considered one of the best technological advances in health that leads us to talk about intelligent operating rooms. With the incorporation of the first Da Vinci, the Hospital de Bellvitge became one of the pioneer hospitals in robotic surgical interventions in Spain. The Da Vinci robot is a computerized instrument that allows the surgeon’s visual capacity to increase 10 to 20 times. It has four arms and robotic hands, capable of performing micro movements with absolute perfection and turning 360 degrees, allowing it to reach delicate places in our body.
It is already used in neurological, gynecological, urological or cardiothoracic procedures, but also in other surgical processes. It makes interventions more comfortable and more precise, especially the most complex and difficult to access, overcoming the limitations of laparoscopic surgery.
Robotic surgery is a method of performing surgery using small tools attached to a robotic arm. The surgeon controls the robotic arm with a computer.
The benefits: The surgical tools used in robotic surgery are much smaller than those used in open surgery. Since the incisions are smaller, bleeding is less and there is less trauma during the procedure, which also means less pain after surgery and less scarring.
The risks: Surgeons using a robot do not receive the tactile feedback that comes from directly cutting a patient’s tissue, and that can increase the risk of injury by affecting adjacent organs. The machine can also cause burns from electric current.
Robotic surgery is recommended: The medical specialties indicated for the surgical use of the Da Vinci® robot are: urology, certain gynecological pathologies, general surgery, cardiothoracic surgery, pediatric surgery, otorhinolaryngology and some indications of neurosurgery.
The Da Vinci robot aims to strengthen the surgical skills of doctors and offer patients the option of a minimally invasive intervention, even when it is a highly complex procedure.
https://www.google.com/search?q=cirujia+robotica&oq=cirujia+robotica&aqs=chrome..69i57j0i10i512l3j0i10i22i30i625.14165j0j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8
Los diez avances médicos de la primera década del siglo XXI.