Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a herpes group virus that affects humans. It can cause serious health problems for people with a weak immune system and babies of women who become infected during pregnancy. The major problem of cytomegalovirus in adulthood is that it produces serious clinical symptoms in people with immunodeficiency (weak immune system) such as those who are transplanted or those who have HIV infection without antiretroviral treatment.
This virus can be transmitted through various routes because it is excreted through urine, saliva, vaginal secretions, semen and breast milk. The contagion is usually produced by direct contact of a person with the fluids of an infected, and transmission can occur from mother to child in pregnancy, during delivery or breastfeeding.
The virus is introduced into people by the respiratory mucosa or the genitourinary tract. Also if you touch the remains of saliva from an infected and then put your hand to your mouth. In the fetus the virus enters through the blood. Although antibodies against the virus are produced and lymphocytes fight against it, in people with immunodeficiency and fetuses this response is usually not enough to control the infection.
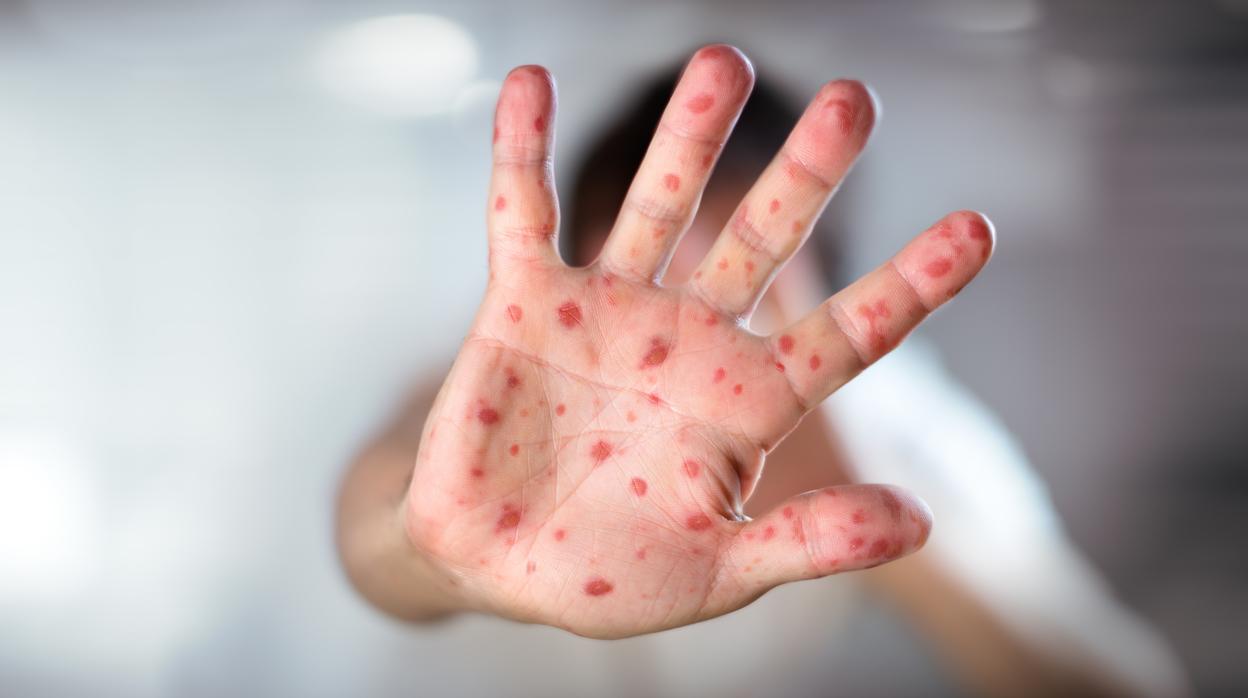
If there are symptoms of cytomegalovirus infection, sore throat, tongue swelling and enlargement of the neck ganglia are milder than in EBV mononucleosis. The most typical sign is fever and the increase of liver transaminases in the analytic.
Even if your baby does not have symptoms of cytomegalovirus infection at birth, you may experience long-term symptoms. For example, hearing impairment, intrauterine growth retardation, encephalitis, and microcephaly may occur.
Pregnant women and their children the danger of CMV is in congenital infection, because it implies the possibility that the child has serious consequences that condition him for his whole life.
Primary infection with CMV during pregnancy is estimated to affect 1-7% of pregnant women.
There are no vaccines for CMV, nor a 100% effective way to avoid infection.
Poor social and economic conditions almost all children have become infected before reaching adolescence because the lack of hygiene and overcrowded conditions favor transmission between people.
Proper hand hygiene is the most important measure to avoid infection. Especially, if you work with groups of children, and after handling diapers or toys, or after cleaning the mucus.
In these cases, you should not share utensils type cups, silverware or dishes with children or family members with the virus.
 Likewise, if you live with an infected person, kissing and sexual contact should be avoided.
Likewise, if you live with an infected person, kissing and sexual contact should be avoided.
It is not recommended to screen pregnant women at the present time, but you should study the immunity to CMV of people with HIV infection or those who are going to receive a transplant.
As for the treatment for congenital infection, the drug ganciclovir should be used, which is administered intravenously. The other option is valganciclovir, which is orally administered. These drugs must be administered for at least six weeks, and with this long-term sequelae can be reduced.
Always take care of your health with a unique and efficient service. Visit Pharmamedic.