[et_pb_section bb_built=”1″][et_pb_row][et_pb_column type=”4_4″][et_pb_text _builder_version=”3.13.1″]
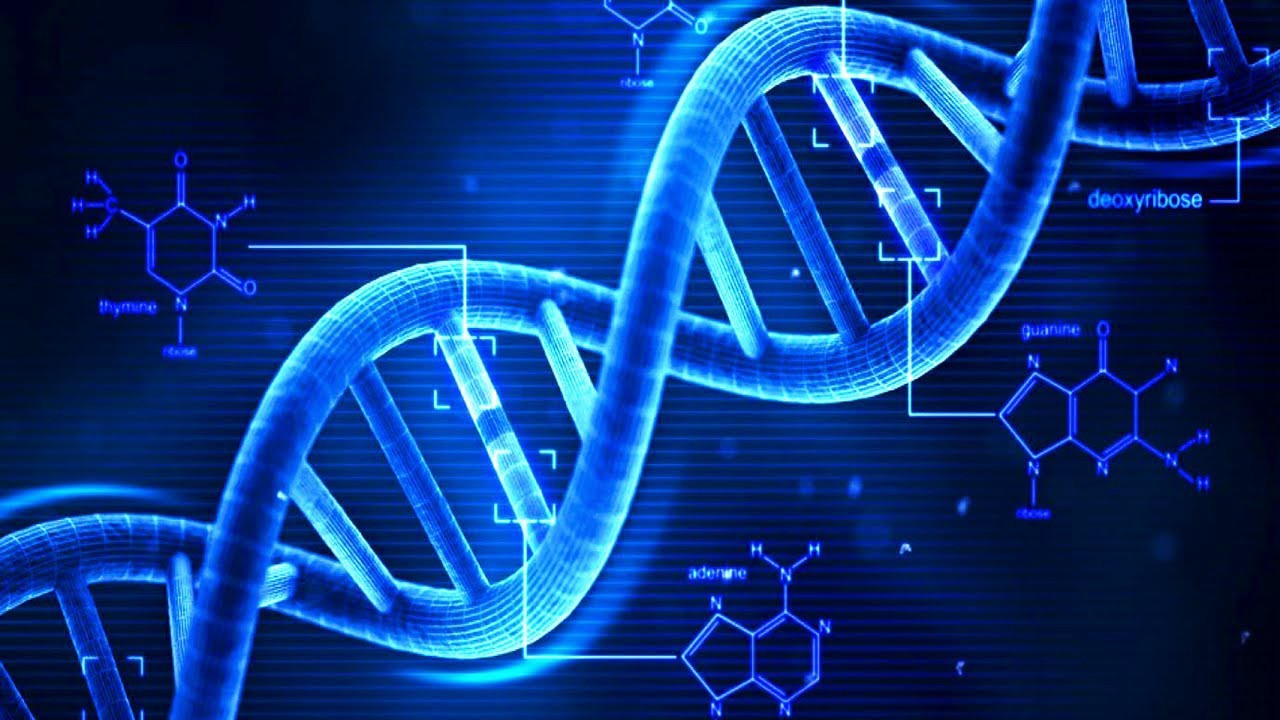
Transcription is the first step of gene expression.
This stage involves copying the DNA sequence of a gene to produce an RNA molecule. Enzymes called RNA polymerases perform transcription, they bind nucleotides to form an RNA chain. Recombinant DNA molecules (rDNAs) are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods known as genetic recombination to gather genetic material from various media, creating DNA sequences that are not otherwise found in the genome.
Recombinant DNA is the general name of a piece of DNA that has been created by the combination of at least two strands. The molecules of recombinant DNA are, in many cases, called chimeric DNA, because they can be made of material from two different species, such as the mythical chimera. This technology uses palindromic sequences and leads to the production of sticky and dull ends.
Recombinant DNA differs from genetic recombination in that its results are obtained by artificial methods in a test tube, while in genetic recombination they are obtained with a natural biological process that results in a remix of existing DNA sequences, essentially , in all organisms.
Well, according to an article published in Technology Review, the production of DNA could revolutionize molecular biology. A Cambridge biotechnology company produces custom-made DNA strands, preventing scientists from having to attach complicated pieces of old-fashioned DNA.
These and other innovations are also possible in Pharmamedic.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]