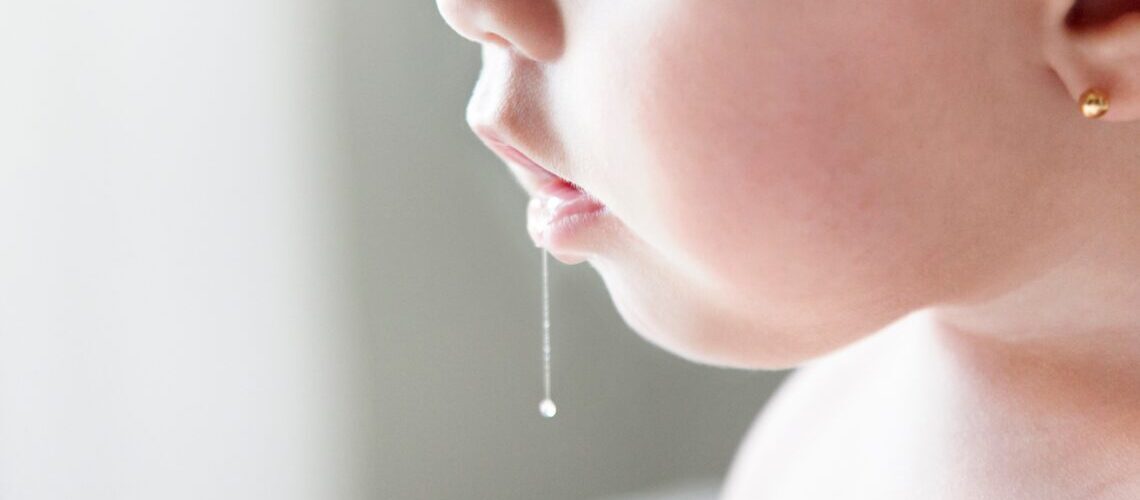
Sialorrhea or chronic drooling is the inability to retain saliva in the mouth.
Sialorrhea or drooling is not usually due to a high production of saliva, but to an alteration in its processing. Sialorrhea, also known as thialism, hypersalivation or chronic drooling, is an oral pathology that consists of the production of saliva at abnormally high levels or the inability of the patient to swallow saliva. It is not considered a serious disease, but it is a condition that It will have a direct impact on your daily life.
CAUSES OF SIALORRHEA, THIALISM OR HYPERSALIVATION:
Sialorrhea can be produced by the consumption of medications such as:
- Clonazepam, Epinephrine, Iodinated Compounds, Carbachol, Bethanechol, Pilocarpine, Neostigmine and Physostigmine, Nitrazepam.
- The inability to swallow saliva due to neurological diseases such as: cerebral palsy, Parkinson’s, facial nerve palsy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Riley-Day syndrome, sequelae of a stroke or brain trauma. serious.
- Other cases caused by dental prostheses.
CLASSIFICATION OF SIALORRHEA, THYALISM OR HYPERSALIVATION:
It can be classified into two types: anterior sialorrhea and posterior sialorrhea.
Previous sialorrhea: produces an incontinence of saliva, that is, drooling.
Posterior sialorrhea: it is the flow of saliva that goes from the tongue to the pharynx.
SYMPTOMS OF SIALORRHEA, THYALISM OR HYPERSALIVATION:
- Continuous drooling. You cannot control saliva levels.
- Desquamation of the lips.
- Muscle fatigue due to forcing the act of swallowing excess saliva.
- Dermatitis in the chin area.
- Taste disturbance.
CONSEQUENCES OF SIALORRHEA, THYALISM OR HYPERSALIVATION:
Sialorrhea causes a series of oral problems such as lip dermatitis or commonly called cold sores. Sialorrhea also causes oral infections such as candidiasis.
THE DIAGNOSIS OF SIALORRHEA, THYALISM OR HYPERSALIVATION:
For the diagnosis of sialorrhea it is simple, clinical tests are not carried out, it can only be observed that a person suffers from sialorrhea if there is continuous drooling in which saliva cannot be controlled in the mouth.
RECOMMENDATIONS TO TREAT SIALORRHEA, THYALISM OR HYPERSALIVATION:
- Cover pillows with a waterproof pad.
- Use a portable suction machine to suction saliva.
- Gargle before going to bed with salt water.
- Reduce dairy, sugar and grain products in the diet.
- Drink plenty of fluids throughout the day: carbonated drinks, juices, tea, iced coffee, among others.
- Frequently drink small sips of water during meals, as well as swallow frequently to aid swallowing.
- Know the origin of the sialorrhea, if it does not respond to alternative treatments, surgical treatment can be used: which consists of the extraction of some salivary glands or ligation of the saliva-releasing ducts. Consult with a specialist.