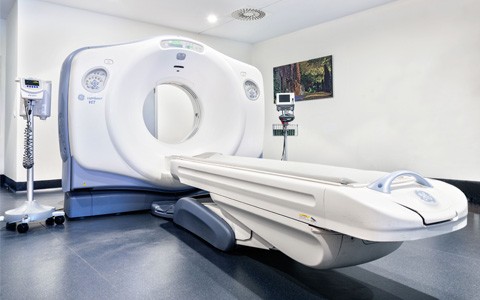
Computed tomography, or CT scanner, refers to a computerized X-ray imaging technique in which a narrow beam of X-rays is projected at a patient and rotated rapidly around the body, producing signals that they are processed by the machine’s computer to generate cross-sectional images, or “slices.” These cuts are called tomographic images and can provide the doctor with more detailed information than conventional ones.
Once several continuous slices are collected by the machine’s computer, they can be digitally grouped or stacked to form a 3D image of the patient that makes it easier to identify the skeleton, organs and tissues, as well as possible tumors or abnormalities.
The CT scanner or CT scanner is connected to an X-ray machine to create a series of detailed pictures of the inside of the body.
The fundamental components of the CT machine are the gantry (the drum of the washing machine, untranslatable), the table (the stretcher where the patient lies) and the operator console.
CT uses X-rays as an energy source. The emission of electrons is achieved by heating a filament with an electric current.
A CT scan is used to diagnose disease, plan treatment, or determine if treatment is working. The Axial or Transversal cut is the one that divides the patient into superior and inferior. The representation of the cuts will always be from top to bottom (with the exception of the skull).
In some cases, to perform these procedures, a dye is injected into a vein or swallowed so that these tissues and organs show up more clearly.
Contrast media have been developed that are highly visible on an x-ray or CT scan and are safe to use on patients.
Complete exams take only a few minutes and if they are more modern devices they can take images of the whole body in less than half a minute. The types of tests that can be performed with computed tomography are named below:
- CT scan of the skull or head
- CT scan of the lumbosacral, cervical and thoracic spine
- Chest CT scan
- CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis
- Computed tomography of the orbit
- CT angiogram
These tests will help the specialist to diagnose some infections, as well as to diagnose pathologies of the spinal cord or spine. Helps diagnose spinal pain. It is used to detect bleeding due to trauma, internal organ injuries or fractures. It helps in the diagnosis of tumors, to see its extension and size. It allows to evaluate and plan the results of a surgery.
The risk that exists when performing a CT scan is that they can present life-threatening conditions, such as bleeding, blood clots or cancer.
https://www.gruposcanner.biz/eu/la-tomografia-axial-computarizada/que-es-y-para-que-se-realiza/