[et_pb_section bb_built=”1″][et_pb_row][et_pb_column type=”4_4″][et_pb_text _builder_version=”3.13.1″]
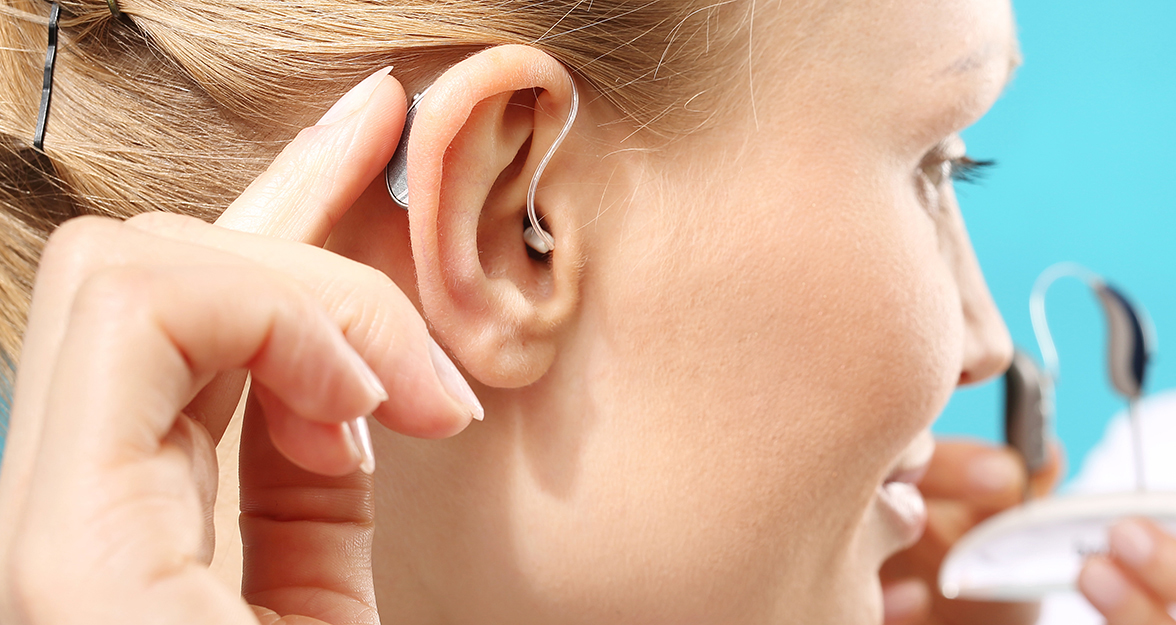
Hearing loss, deafness or hearing impairment, is a sensory disorder that consists of the inability to hear sounds, and that hinders the development of speech, language and communication.
One in every 300 children is born with an auditory deficiency, and one in every 1,000 with a deep bilateral deafness; 74% of children who have language delays suffer hearing loss, and many children with psychomotor retardation and behavioral disorders have mild hearing loss that has not been diagnosed.
Hearing loss depends on three main factors: the intensity of the hearing loss, the location of the lesion, and the time of appearance of the lesion.
A hearing loss can appear both in the prenatal and postnatal period of life, and until late adolescence. According to the moment in which the hearing loss occurs, hearing loss can be:
- Pre-lingual (if it appears before learning to speak).
- Post-linguistic (after learning to speak).
- Perilocutive (when you are learning to speak).
According to the intensity of hearing loss, hearing loss can be classified as:
- Light: with a loss of 20-40 dB; it is characterized by the difficulty to listen to distant conversations or in noisy surroundings.
- Medium: with a loss of 40-70 dB; It is characterized by the difficulty to participate in conversations.
- Severe: a loss of 70-90 dB; they can only listen to very loud conversations and less than 30 cm.
- Deep: a loss greater than 90 dB, they are only able to hear some very intense environmental sounds.
- Infant hearing loss can occur in the period immediately after birth, originated by prenatal or perinatal agents, or in the period between two and four years of age, due to several local infectious agents that cause otitis media.
- In adults, hearing loss or deafness is related to aging and occupational hearing loss due to continuous exposure to loud noise.
The prevention of hearing loss, deafness or hearing loss lies in avoiding as far as possible the presence of the risk factors that cause it. In cases where the hearing loss is genetic, prevention is not possible, but the early detection and implementation of mechanisms for its adaptation and treatment as appropriate.
Always take care of your health with a unique and efficient service. Visit Pharmamedic.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]