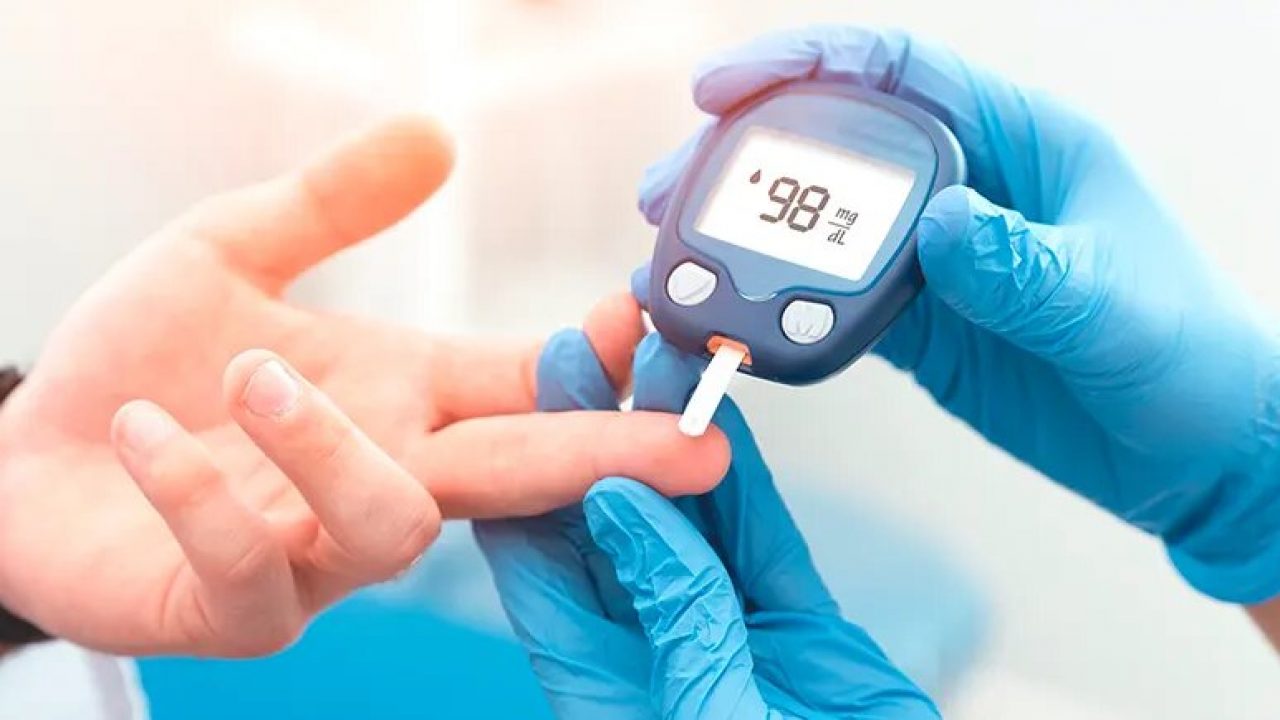
If blood glucose levels are very high or very low, they can lead to acute complications that must be resolved quickly.
High blood glucose levels maintained for a long time cause damage to the arteries throughout the body, and in the long term they deteriorate and alter various organs, especially the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart and other blood vessels.
In the early stages of the disease there may be no symptoms of diabetes.
Glucose is an important source of energy for most cells in the body.
Currently, 4 types of diabetes are recognized: type 1 and type 2. Gestational diabetes and other genetic types.
- Type 1 diabetes: typical in early ages between 30-40 years. In his treatment he usually needs insulin almost always.
- Type 2 diabetes: it is the most frequent, it generally occurs in obese and older people. You do not always need insulin, especially in the early stages of the disease, and can be controlled with diet and antidiabetic drugs.
- Gestational diabetes: pregnancy is a situation that favors poor blood sugar control and can lead to gestational diabetes. For this reason, approximately at week 28 of pregnancy, a special test is performed on all pregnant women, to assess whether there is diabetes. Although a return to the non-diabetic state is generally achieved after pregnancy, there is a risk of frank diabetes over the years.
- Other specific types of diabetes: those caused by some genetic defects of the beta cells, genetic defects in the action of insulin, diseases of the exocrine function of the pancreas such as cystic fibrosis, and that secondary to the use of some medications.
Common warning signs of diabetes are:
– Polyurin (urinate a lot).
– Polydipsia (excessive sensation of thirst).
– Tiredness and drowsiness.
– Reduced visual acuity.
– Weightloss.