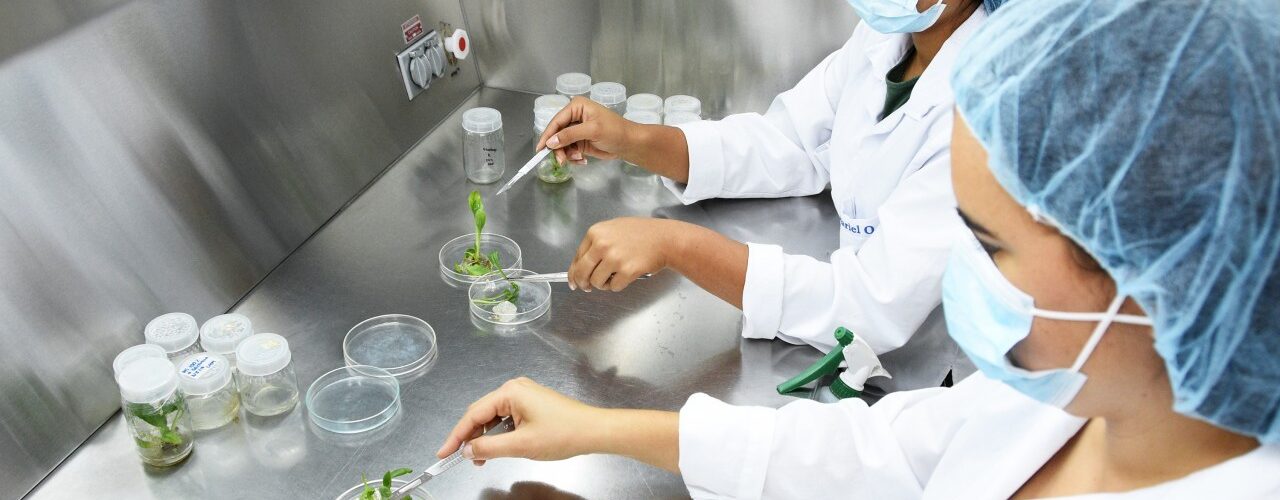
Plant biotechnology is currently applied in disease control.
Through plant biotechnology, we can achieve disease control thanks to numerous techniques, such as:
- Production of secondary metabolites.
The metabolites normalize the relationships of the plant with the environment that surrounds it and have therapeutic use as an analgesic, anti-smoking therapy, antimalarial, antitumor, cardiotonic and as a laxative.
Likewise, these metabolites are used in the commercial production of dyes and fragrances.
- Plants as bioreactors
These modify plants for biopharmaceutical purposes for the synthesis of vaccines and antibodies, among other uses.
- Other techniques such as:
Tolerance to abiotic stress, phytoremediation, production of compounds of industrial interest.
On the other hand, plant biotechnology makes it possible to improve plant varieties based on characteristics of agricultural and ornamental interest.
The benefits of biotechnology in the food industry
It is used to produce foods with healthy properties, such as yogurts with probiotic bacteria, milk enriched with calcium, or foods low in trans fats, these functional foods help improve health and prevent diseases.
Biotechnology is applied in medical, agricultural research and animal production, among other areas vital for development, as well as in the production of some food items.
Therefore, its purpose is not only to increase production, improve or modify functionality, but also to meet consumer demand for safer, fresher and tastier products.
On the other hand, edible vegetable oils have polyunsaturated, monounsaturated and saturated fatty acids in their composition in different proportions. Many plant oils are used to make soaps, skin products, candles, perfumes, and other personal care and cosmetic products.
Likewise, the chemical composition of vegetable oils corresponds in most cases to a mixture of 95% triglycerides and 5% free fatty acids, sterols, waxes and other minor components.
Oil can be extracted directly with solvents from products with low oil content, such as soybeans, rice bran and corn. After sterilization, the pulp is removed before being subjected to mechanical pressure often in a lathe press.
Oils are liquid fatty acids at room temperature (with the exception of palm and coconut oils), used in cooking, for dressings, fried or grilled. Less common is the use of butter, a saturated fat that should be avoided when frying foods.
The very abundant nutrients in the oil are: oleic acid is its main component since it represents more than 55% of the fatty acid content. As well as, the main vitamins that extra virgin olive oil contains are vitamins A, D, E, and K.
That is why the Spanish Pediatric Association recommends the consumption of this oil from ages 2 to 6 as the main fat in a child’s diet.
Many vegetable oils are a healthy source of energy and some are even considered essential for the functioning of the human body, since they are the precursors of hormones and even some neurotransmitters, without which we would not be able to function or survive.
Best-known types of vegetable oils:
- Soy oil.
- Safflower oil.
- Rapeseed, canola or rapeseed oil.
- Oil Grape.
- Sunflower oil.
- Olive oil.
- Coconut oil.
- Corn oil.
Vegetable oils, nuts and fish contain mainly unsaturated fats. There are two types of unsaturated fats: monounsaturated and polyunsaturated.
Applications of plant biotechnology:
- Improvement of varieties based on characters of agronomic interest:
- Phytoremediation: elimination of contaminants.
- Biofuels: bioenergy crops (1st, 2nd, 3rd generation)
- Biofactories: biopolymers, therapeutic proteins, biodegradable plastics, etc.
Extra virgin olive oil is the healthiest and recommended for regular use in cooking. Seed oils, such as sunflower, and coconut oil should be consumed in moderation due to their high saturated fat content.
Certainly, the best oils for cooking and frying foods are: Olive oil, avocado oil and canola oil.
Therefore, the benefits of oil are primarily to transport fat-soluble vitamins and the intake of fats and oils is necessary for health.
FONT
https://www.scielo.cl/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0717-75182012000300014
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biotecnolog%C3%ADa_vegetal