[et_pb_section bb_built=”1″][et_pb_row][et_pb_column type=”4_4″][et_pb_text _builder_version=”3.13.1″]
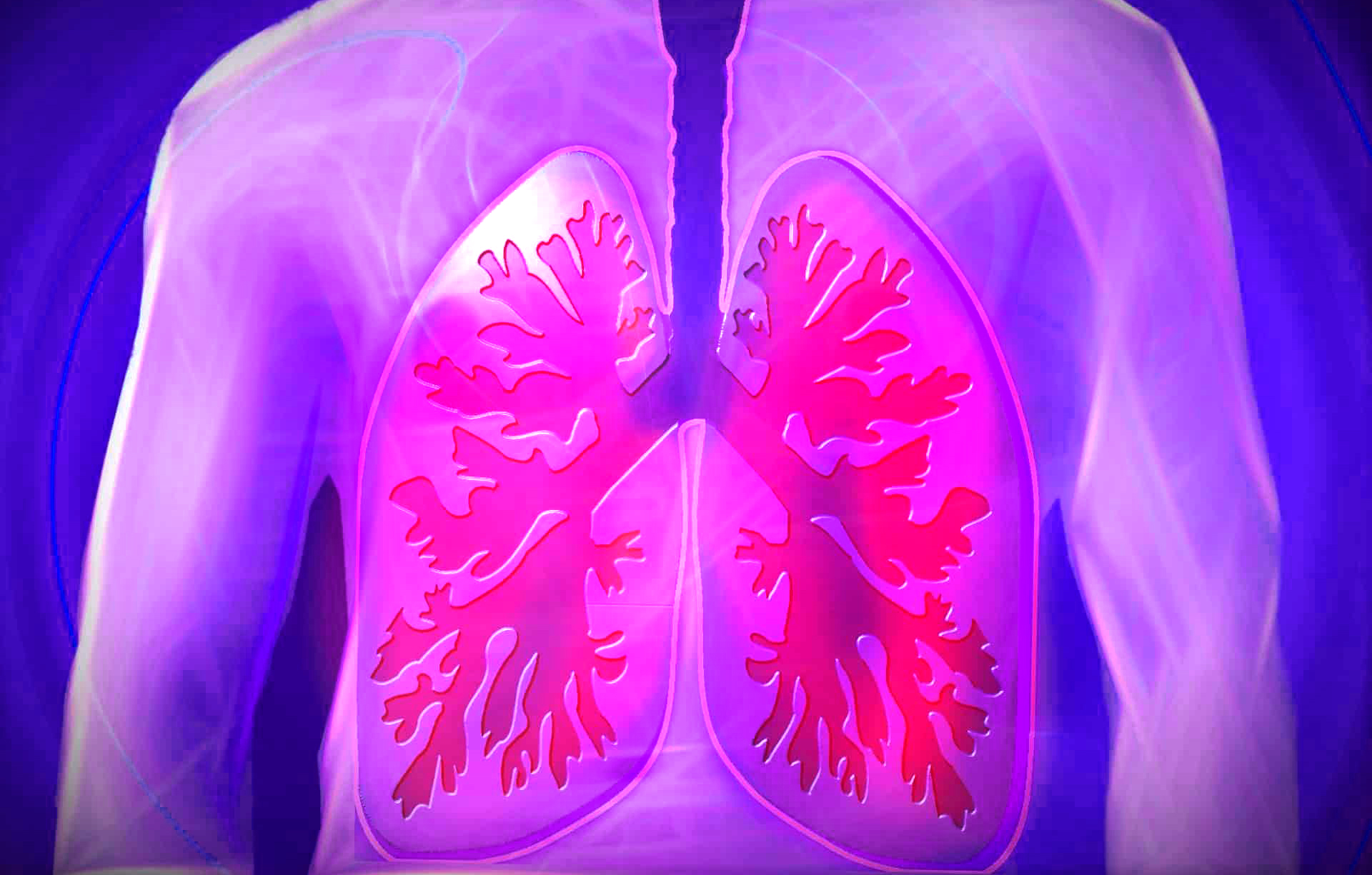
Pulmonary edema is the accumulation of fluid inside the lungs.
The lungs fill with fluid when the blood that is normally inside the blood vessels exits outward, flooding the pulmonary alveoli. This only happens when something is wrong in the lungs or in the heart; thus, we can divide the lung edema into the following types:
- Cardiogenic lung edema
- Non-cardiogenic lung edema
- Neurogenic pulmonary edema
The symptom common to all types of pulmonary edema is the sensation of shortness of breath, or dyspnea, whose severity depends on the causes that have caused the condition, and which must be identified as soon as possible.
The most common cause of pulmonary edema is usually congestive heart failure, which in turn can be caused by a sudden rise in blood pressure, aortic valves, or heart attacks or myocardial problems. However, pulmonary edema can also be due to other causes, such as taking certain drugs, kidney failure, lung damage caused by poisoning or infections.
To treat pulmonary edema itself, it is necessary to avoid reducing the concentration of oxygen in the blood (support treatment), which can be achieved in the following way:
- Oxygen should be administered in a mask to all patients with acute pulmonary edema.
- PEEP: is a device that transmits positive pressure to the lungs.
- Mechanical ventilation: only if the above measures do not work.
Always take care of your health with a unique and efficient service. Visit Pharmamedic.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]