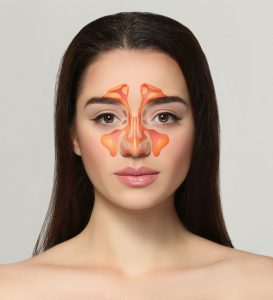
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the paranasal sinuses (hollow cavities that are located in the bones that surround the nose) due to an allergy or a viral, bacterial or fungal infection.
The most frequent cause of sinusitis are viruses, mainly rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, and influenza viruses (influenza) or parainfluenza among others.
Possibilities that exist of suffering sinusitis:
- Have suffered a cold.
- Certain medications, such as prolonged use of decongestant sprays.
- Nasal obstruction due to:
- Abnormalities of the facial bone.
- Deviated partition.
- Cleft palate.
- Polyps, tumor or allergies.
Sinusitis includes three factors:
- Obstruction of the exit orifice of the sinus, for example by inflammation of the mucosa due to infection or allergy, or when there is a nasal polyp
- The reduction of the movement of the cilia that are in the epithelium that covers the breasts, and that normally cleanse the breasts when mobilizing the respiratory secretions. This occurs in some diseases of genetic origin, such as Kartagener syndrome, but also by exposure to tobacco, some medications, chemical compounds, infections, allergies, and so on.
- The increase in the viscosity of secretions that occurs in some diseases such as cystic fibrosis.
 There are certain factors that increase the possibility of suffering from sinusitis. These are:
There are certain factors that increase the possibility of suffering from sinusitis. These are:
- Age: both young people and the elderly are more susceptible to sinusitis.
- Sex: women are usually more likely to have sinusitis than men.
- Environmental factors: such as traveling at high altitudes, or air pollution.
- Smoking: the increase in the possibility of suffering sinusitis occurs in both active and passive smokers.
- Certain activities: for example, flying or swimming.
The treatment of acute bacterial sinusitis can be used amoxicillin, clarithromycin or azithromycin. In case the evolution is not good, second-line antibiotics such as amoxicillin / clavulanic acid, cefuroxime, levofloxacin, and so on are used.
The cases of sinusitis caused by dental infections require specific treatments against bacteria called anaerobes that are usually involved in this type of infection.
The treatment of sinusitis is administered for one to two weeks.
Sometimes it is necessary to administer antibiotics intravenously to the most serious patients and with symptoms of general affectation.
In case of nosocomial sinusitis (infection contracted in the hospital), the most common pathogens are Staphylococcus aureus and gram-negative bacilli; in these circumstances it is convenient to practice sinus cultures to guide the treatment. Initially, a broad spectrum intravenous treatment is applied, which will later be adapted to the culture results.
As for fungal sinusitis, they are treated with surgery and the use of antifungal drugs
Always take care of your health with a unique and efficient service. Visit Pharmamedic.