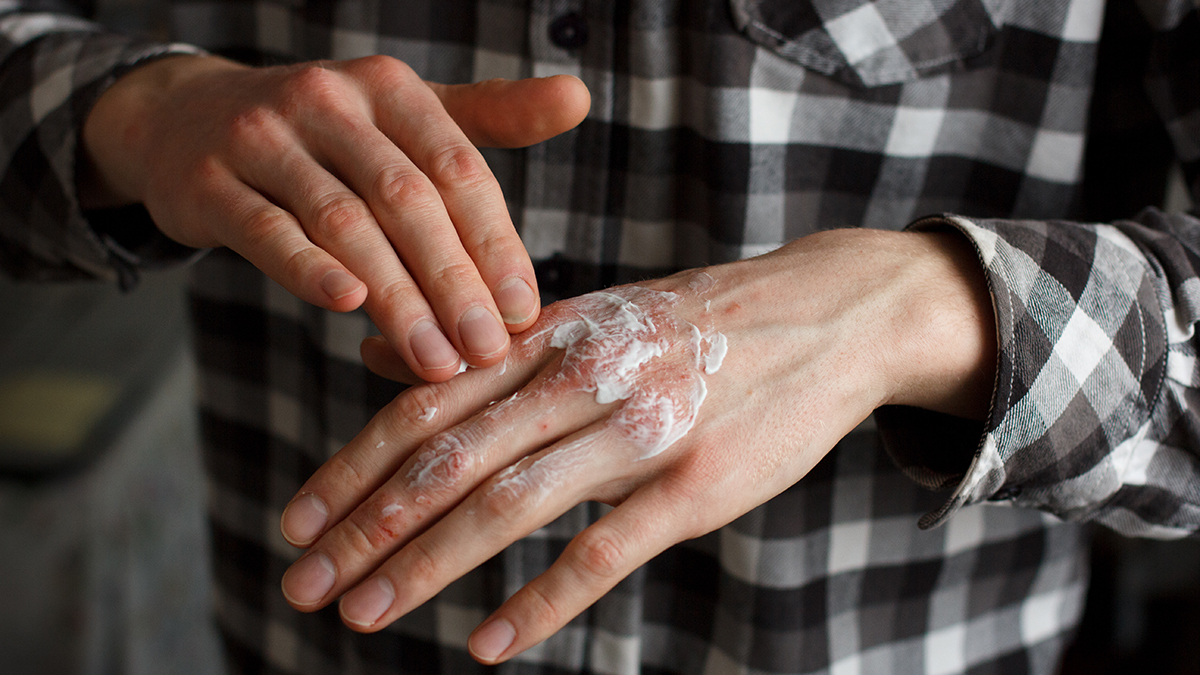
Psoriasis is located mainly in the areas that cover the joints, the scalp, the groin and the lower part of the back.
Psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of reddish inflamed areas covered by plaques of flaking skin. In general, there are usually no serious complications, although sometimes it can be painful.
The lesions can be located in different parts of the body; The most common is to find them on the trunk (especially on the back), extremities and scalp, but there are also cases in which they affect areas such as the armpits, genitals, navel, and even under the nails. It is not common, but psoriasis can sometimes cause itching and, in the most severe cases, pain.
The goal of treatment is primarily the reduction of symptoms and the prevention of secondary infections.
For this, there are three treatment options for psoriasis: substances for topical use, systemic drugs and phototherapy.
Psoriasis is initially treated with products that are applied directly to the skin.
- Creams or lotions with coal or anthralin. Anti-dandruff shampoos. Humectants. Keratolytics; products that remove excess skin thus reducing flaking. Vitamin D analogs, prevent the proliferation of keratinocytes (skin cells that accumulate forming plaques Retinoids; vitamin A derivatives. They have similar efficacy to vitamin D-based products. Topical corticosteroids; corticosteroids are immunosuppressants, so their use is only recommended in cases of mild psoriasis.
- Natural treatments: Aloe vera and pita. Both with emollient properties. Dye moth or traitor root. Plant of the Boragenaceae family; Like the previous ones, it has emollient properties, which is why it has been traditionally used to alleviate the symptoms of different skin pathologies.
Systemic drugs
These types of drugs act from within the body; They are usually administered orally, although some can also be found in injectable form.
- Medicines with vitamin D or vitamin A (retinoids, such as Acitretin).
- Cyclosporins, immunomodulators.
- Biological drugs. (etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, and ustekinumab).
- Anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative effect. It is the most widely used systemic drug.
Phototherapy
The treatment is based on controlled exposure to ultraviolet light (UVA or UVB). This method reduces inflammation and slows the rate of skin cell production in people with psoriasis. High efficacy in clearing lesions and prolonged remission of outbreaks has been observed. The drawback is that it requires a minimum of 20 treatments, with 2 to 4 weekly visits, followed by maintenance treatment at variable intervals.
There are several application options for this treatment:
- Broadband UVB.
- Narrowband UVB.
- UVA + psoralens (PUVA): reduction of the influx of lymphocytes and stimulation of the formation of melanocytes.
Tips for psoriasis patients
- Moderate sun exposure.
- Take baths in the sea.
- Use moisturizing creams on a regular basis, especially based on natural products such as oatmeal or calendula.
- Leave wounds uncovered, in the air, whenever possible.
- Avoid the consumption of fatty meats and increase the consumption of fruits and vegetables.
- Avoid the consumption of alcohol and tobacco.
- Drink plenty of water to keep the body hydrated.
- Try to follow healthy lifestyle habits, avoiding stress situations as much as possible.
- Due to its social and aesthetic impact, it can reduce self-esteem, so it may be necessary to require help or psychological assistance.