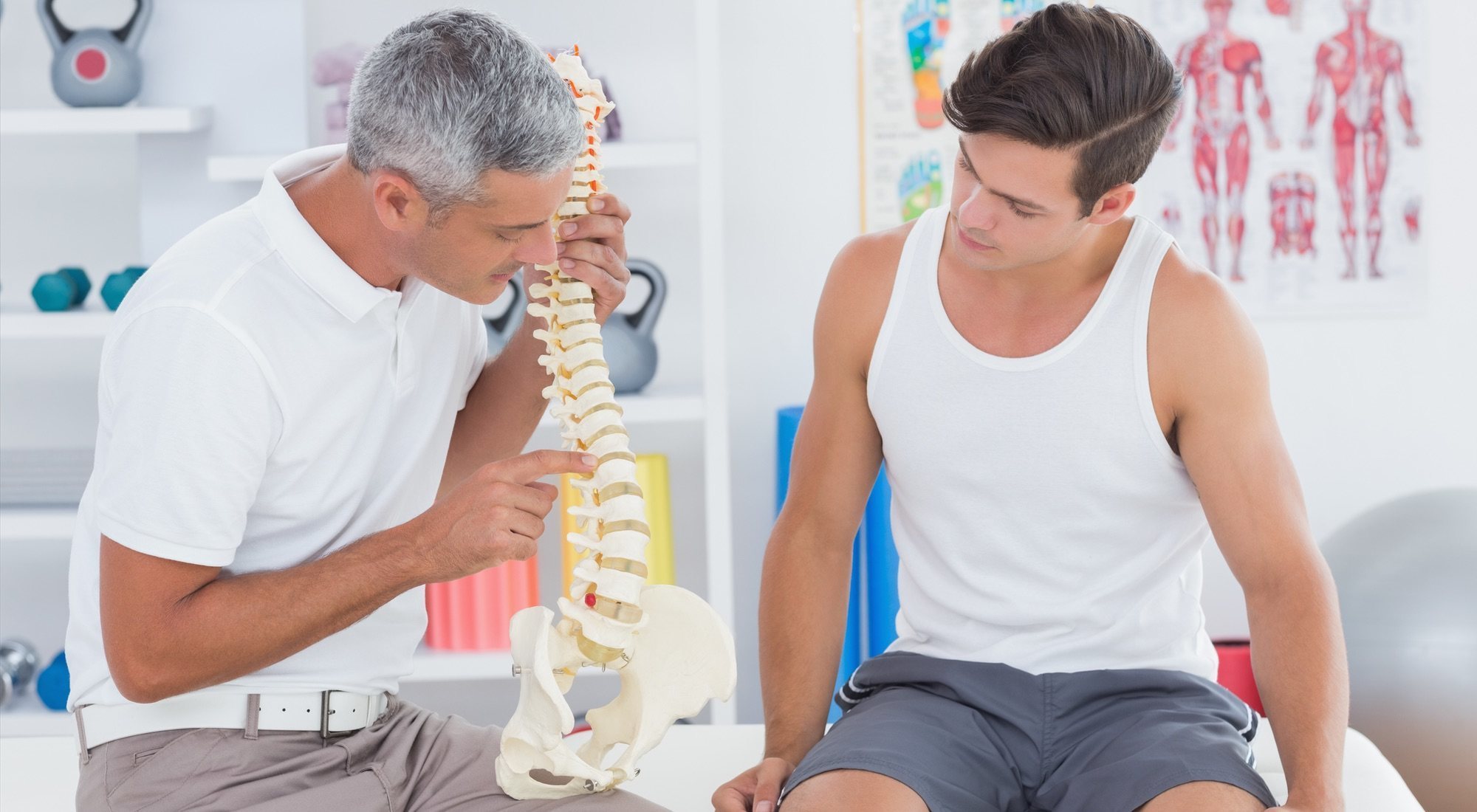
Pubalgia, also known as pubic symphysis or dynamic osteopathy of the pubis, is defined in its strict sense as inflammation of noninfectious origin of the symphysis pubis.
It is generally considered an overuse injury, which creates a stress reaction in the pubic symphysis and adjacent bone tissue. Pubalgia is a pain that is very common in athletes who play soccer. This can be an acute pain, located at the pubic symphysis, with possible irradiation to nearby areas, preferably groin, lower abdomen, perineum and hip. To be able to perform a specific treatment for this type of pain in the pubis, it will be necessary to carry out certain assessment and evaluation steps, in order to obtain a good diagnosis, and apply the appropriate treatment to treat this pain that can be very annoying and that It may even require surgical intervention.
Epidemiology of Pubalgia
Within the football field, which corresponds to the sector where this type of injuries most affects, the registered annual incidence oscillates, according to demographic data between 12-16%. It is also frequent the appearance in ice hockey, rugby, American football, Australian football and runners in the background (4)
The most common entity in the groin injuries are related to the adductors, followed by those related to the iliopsoas and then in relation to the abdominals.
Lesion mechanism
It is usually associated mainly with repetitive striking gestures (such as kicking a ball). In the case of chut there is a repetitive hyperextension of the trunk together with hyperextension and hip abduction. This will produce shear through the symphysis pubis and anterior of the pelvis, especially if there is a muscle imbalance, this striking action causes asymmetries in the lumbar musculature and in the iliopsoas.
In the conservative treatment and prevention, whether primary or secondary, there is no differentiation of objectives between them. It will focus on a specific work valid both for post-injury rehabilitation and for prevention (very important).
In the first place, the sports activity will be interrupted, the treatment will focus on the elimination of pain and will continue with muscular training programs. These exercises will focus mainly on the strengthening of adductors, going from the most static to the most functional. Lumbo-pelvic strengthening with core exercises and motor control is also very important.
Exercises to work the core and the adductors, the need to give stability to the symphysis of the pubis is highlighted so that the transfer of forces that come together in the joint is effective and coordinated. It is also part of the objectives to recover the range of joint movement of the hip in its rotations and of the lumbo-sacral and sacral-iliac joints, and to treat pain from its root and not with a palliative objective.
Learn more about your health and well-being at Pharmamedic.