[et_pb_section bb_built=”1″][et_pb_row][et_pb_column type=”4_4″][et_pb_text _builder_version=”3.13.1″]
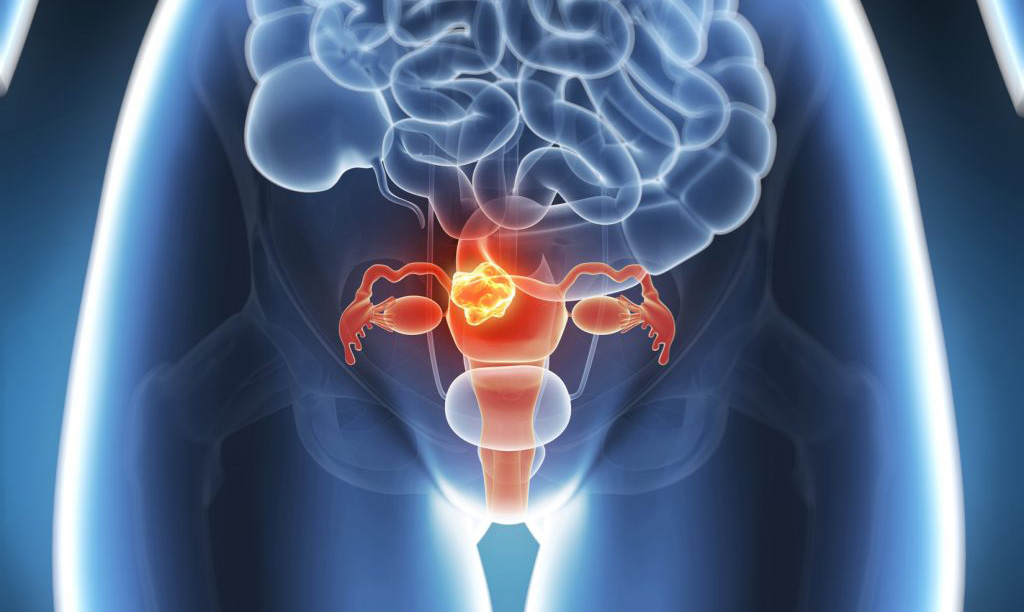
Fibroids are benign and frequently asymptomatic tumors that are formed as a result of an altered proliferation of the muscle fibers of the myometrium (muscle layer of the uterus), dependent on female hormones, and are the most frequent benign neoplasm of the female genital tract.
They affect the uterus in its shape, volume and function.
The characteristics of fibroids are:
- Number: they can be single or multiple, which is more frequent.
- Size: very variable, from very small, to some that weigh several kilos (the largest extirpated weighed about 60 kilos).
- Location: usually located in the uterine body, but could be in any area of the uterus.
They are one of the most frequent causes of secondary dysmenorrhea in this stage of women.
The causes of fibroids are not known, but there are biological reasons for their appearance. These include an increase in the receptors of the uterus to estrogen, probably of genetic origin, and some hormonal changes during menstruation.
Uterine myomatosis is usually diagnosed in the third and fourth decade of life. Fibroids are very rare before puberty, and after menopause new fibroids do not usually appear and those that the patient has at that time will probably decrease in size, although they do not disappear.
Although there are several forms of treatment, only with their extirpation is it possible to make them disappear, and this will be done when they provoke intense bleeding or are the reason for abortions or infertility.
Hemorrhage and pain are the most frequent symptoms of a uterine myoma and are characterized by more abundant and prolonged periods, with the presence of clots on many occasions.
The existence of the myoma can be known before pregnancy. In any case, the diagnosis of the myoma in pregnancy, as well as its growth, is carried out by physical examination and by ultrasound, as in the cases in which they occur outside of pregnancy.
During the routine examination of the pregnant woman, the existence of fibroids could be suspected when the uterus is greater than the one corresponding to the gestation period, and in some cases by palpation.
Ultrasound, which is now a routine method, allows to see the number and size of fibroids and to determine their location, and the evolution during pregnancy.
The incidence of abortions is higher due to the difficulties that the fertilized ovule has to implant in the uterus.
- Increase in premature births (for the same reason as in the previous case).
- Fetal development can be altered.
- Myoma degenerations can occur, as well as modify the location of this.
Complications in childbirth
- Hemorrhages.
- Alterations in the expulsive, if the myoma obstructs the birth canal.
- Alterations in the contractibility of the uterus.
- Alterations in the presentation of the fetus.
In childbirth there is an increase in the number of caesarean sections due to alterations in uterine dynamics (ie contractions), to an increase in previous placentas and alterations in the position of the fetus and obstructions of the birth canal.
Always take care of your health with a unique and efficient service. Visit Pharmamedic.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]