Hormones are proteins or substances made by the body that help control how certain types of cells work.
The effects of hormones in the body are:
Growth and development.
Influences metabolism
The sexual function.
The reproduction.
mood
The side effects of each patient may be different, and will depend on the type of hormone therapy that is applied, among other factors. Knowing about possible side effects is very important for treatment decisions. It is also important to calculate the benefits and risks of any treatment. Talk to a specialist about any questions you have about hormone therapy.
Hormones are powerful. Only a small amount is needed to cause major changes in cells or in the entire body.
The female sex hormones produced by the ovary (estrogen and progesterone) are substances that, through the blood, carry messages to all the organs of the female genital tract to achieve their proper function.
Among its functions are: Fertilization, regulate cholesterol level, protect bones and stimulate libido, also help the formation of collagen.
The estrogens that are produced in our body are called endogenous estrogens, while the estrogens that are administered as drugs are often called exogenous estrogens or synthetic estrogens (if they have been made or altered pharmacologically).
Synthetic estrogens differ slightly from endogenous estrogens in their chemical structure.
Synthetic estrogens are most often used in hormonal contraceptives and as part of hormonal therapies to mitigate the unwanted side effects of menopause.
The side effects of any hormonal contraceptive can be attributed to the difference between the hormone levels produced naturally in the body and the hormone levels of the contraceptive.
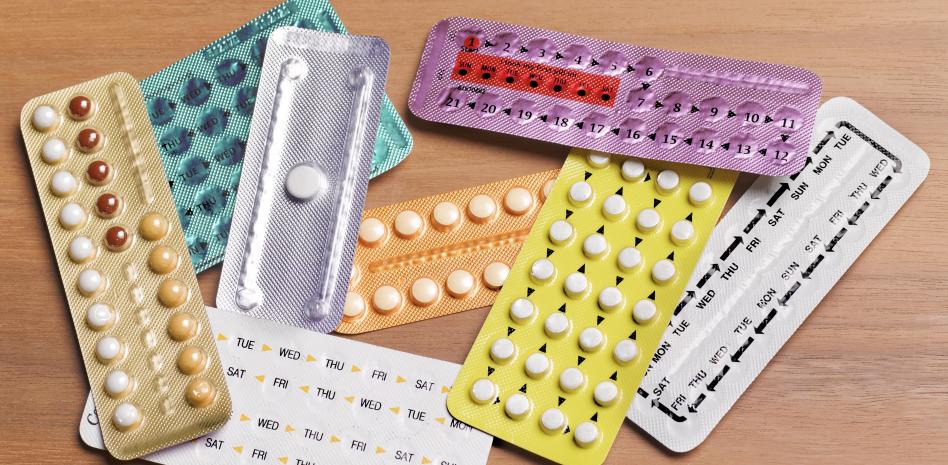
Hormone therapy comes in different forms, such as:
Pills or tablets (orally).
nasal spray
Skin gel and skin patches, applied to the thigh or abdomen
Vaginal creams or tablets to help with dryness and pain with intercourse
vaginal ring
If you experience vaginal bleeding or other unusual symptoms during hormone therapy, see your doctor.