Choking happens when someone’s airways are suddenly blocked and they can’t breathe.
Choking can be caused by poor swallowing of food or by objects getting stuck.
The type of action to reverse it must be different if it is a partial choking or if it is a total choking, therefore, the first thing is to know how to recognize each case:
- Partial choking: we will realize that the pathways are not totally obstructed because the person will begin to cough and make noises, and we will hear their forced breathing. He will put his hands to his throat, an unequivocal sign of choking.
- Total choking: the person will not be able to make any noise since the foreign object will not allow air to enter or exit. Normally the victim is unable to breathe, his skin begins to pale at first and later turns bluish, he can become agitated and lose consciousness. Without proper care he can die.
The technique to do it is as follows:
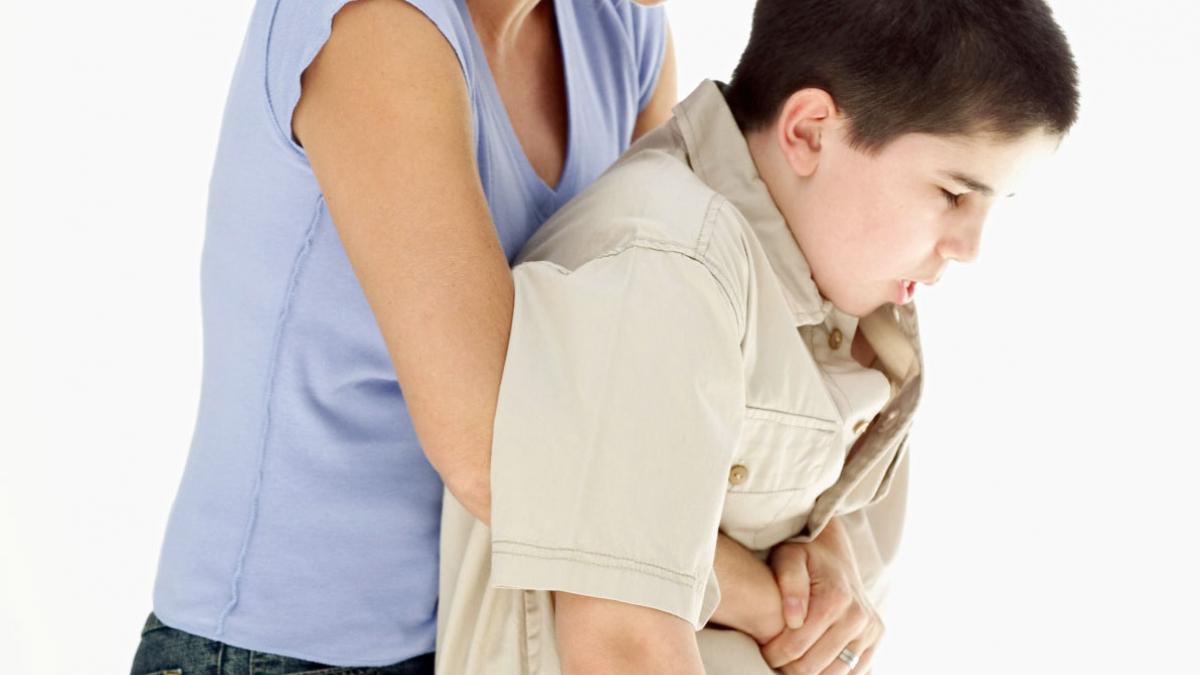
- Stand behind the person while you are standing.
- Put your arms around the waist: the right hand in the form of a closed fist on the upper part of the affected person’s abdomen (at the level of the pit of the stomach, where the ribs meet), and the left hand taking the fist, encircling the base of the chest with the arms.
- Press the abdomen sharply and strongly upwards with both hands.
- Suspends compression.
- Repeat the maneuver as many times as necessary until the person expels the foreign body from their throat or loses consciousness.
- If you lose consciousness, call for help immediately at the emergency telephone number, briefly and clearly communicating what has happened.
- In children older than one year, the same procedure as above is used, but the fist is placed over the child’s navel with the side of the thumb towards the abdomen.
- If a person is alone and is suffocating due to objects that obstruct the airway (trachea), the Heimlich Maneuver can be used on oneself, pinning or positioning the weight of the body on the back of a chair, in this way the pressure within the chest is rapidly increased, forcing the object out of the airway.
- If the above steps are followed correctly, choking can be managed, but the emergency services should be notified if the victim does not expel the choking object and loses consciousness.
- Similarly, it may be that some remains of the object or food that caused the obstruction has remained and may cause discomfort later. If the affected person notices problems swallowing or swallowing, coughs frequently, etc., it is advisable to go to the Emergency Department to be examined by a doctor.
What not to do:
- Abdominal compression can cause injury, so it should not be performed on people who are not choking.
- Giving first aid is not recommended if the person is coughing forcefully and can speak, as a forceful cough may dislodge the object.