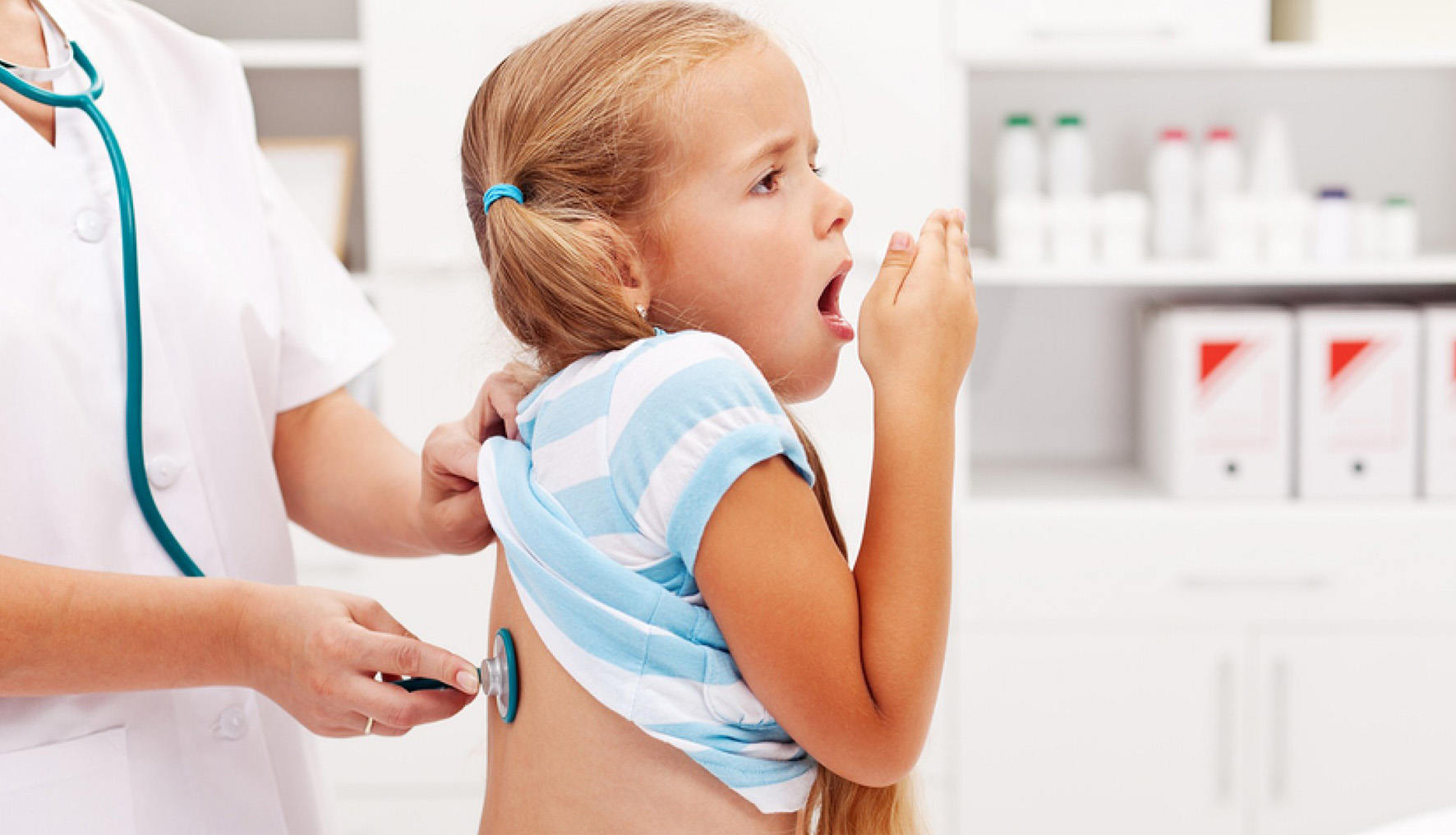
Whooping cough is an acute infectious-contagious disease that affects the respiratory system.
Its main symptom is violent coughing in fits or paroxysms that can make breathing difficult.
The contagion is made directly from the sick person to the healthy person through the air, when speaking or coughing, essentially, by the drops of Pflügge.
One of the characteristics of this disease is that you can often hear a deep convulsive sound when the patient tries to inspire. This disease is caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis or Bordetella parapertussis, exclusively human pathogens that can affect individuals of all ages and cause permanent disability in babies and even death.
The clinical manifestations of whooping cough are similar to the common cold. These symptoms usually appear when a week has passed since the exposure of the bacteria. In the case of children, everything ends in most cases in a rattle, a sound that occurs when the patient tries to take a breath. It is rare that it appears in children under 6 months and in adults. Other common symptoms are: diarrhea, mild fever and runny nose.
Whooping cough stages:
- Incubation period: Lasts between 1-2 weeks. In this period the patient usually does not present symptoms.
- Catarrh or start period: lasts 2 weeks with catarrhal symptoms (rhinitis, sneezing, low-grade fever (if any), tearing, mild cough, dry and irritative, which is becoming increasingly intense.
- Period of convulsive or asphyctic state: lasts about 4-6 weeks takes a deep breath and begins with a cough with blows, uninterrupted, run over, which hinders breathing.
- Period of convalescence or remission: Lasts between 1-3 weeks they become less frequent until disappearing.
Always take care of your health with a unique and efficient service. Visit Pharmamedic.