[et_pb_section bb_built=”1″][et_pb_row][et_pb_column type=”4_4″][et_pb_text _builder_version=”3.13.1″]
Acute pyelonephritis is defined as the infection of the upper urinary tract that affects the pelvis and renal parenchyma.
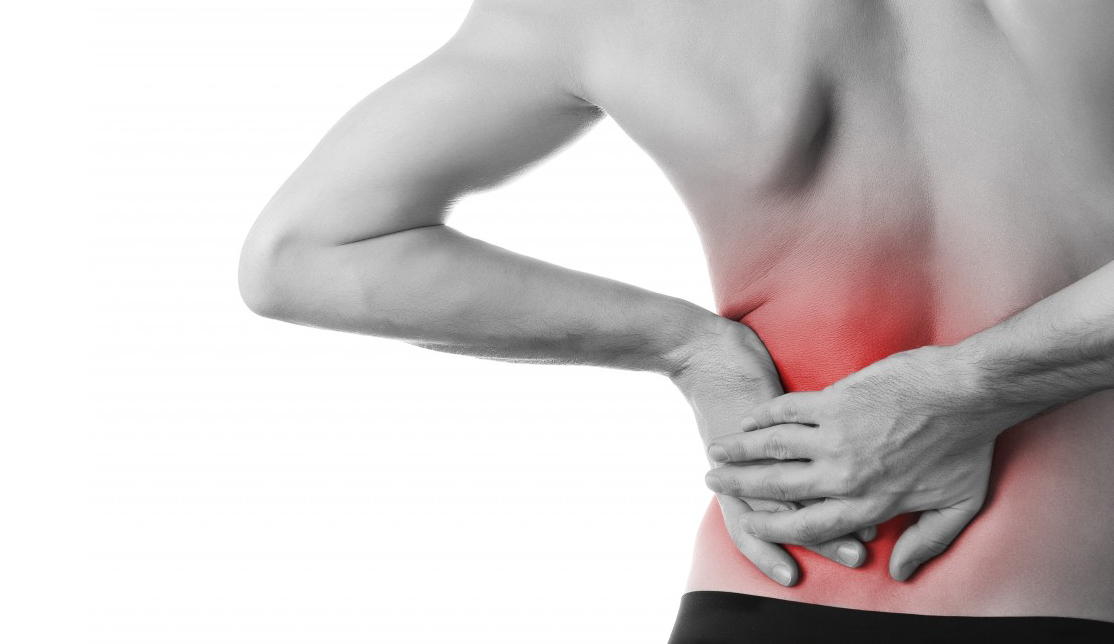
Your symptoms: back pain, fever and chills. Acute pyelonephritis is divided into complicated or uncomplicated; the presence of recurrent cystitis, stones (stones) in the kidney or alterations in the normal form of the kidneys or urinary tract increase the risk of developing this disease.
The cause of acute pyelonephritis is the rise of microorganisms from the fecal flora through the ureters, which are the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder.
The most frequent symptoms that appear in patients with pyelonephritis are the following:
- Fever (body temperature greater than 38.5ºC) and chills.
- Pain in the lower back, although it can sometimes radiate to other areas of the abdomen. If the pain is of the colic type (spasmodic, intense, that begins and ends suddenly) and radiates towards the groin, it suggests the presence of renal lithiasis (presence of stones or kidney stones).
- Nausea and vomiting. Decreased appetite.
- Headache.
Up to 30% of patients have symptoms of lower urinary tract infection, which may precede symptoms of pyelonephritis in 1 or 2 days. These symptoms are:
- Increase in the frequency of urination, but of small amount (frequency).
- Stinging or pain when urinating (dysuria).
- Sensation of not having urinated completely (bladder tenesmus).
- Sensation of not being able to contain urine and having the urge to urinate urgently due to the risk of urinary incontinence (urinary urgency).
- Abdominal pain in the lower abdomen.
If there is a suspicion of pyelonephritis, the following additional tests should be performed: blood test, urinalysis, urine culture or urine culture, blood culture or culture of a blood sample, imaging tests (radiography), abdominal ultrasound.
Since it is a disease of infectious cause, the fundamental treatment of acute pyelonephritis is based on the administration of antibiotics, either orally or intravenously, depending on each case.
Apart from antibiotic treatment, it is important to establish general measures, such as:
- Rest in bed, if there is affectation of the general state.
- Abundant fluid intake (about three liters a day), to increase the amount of urine. In case of obstruction of the urinary tract, the patient’s hydration must be done with great caution, because if complications can not appear.
- Administration of drugs to reduce fever and to relieve pain.
If there are other associated symptoms (vomiting, etc.) these will be treated with the appropriate drugs for this.
Always take care of your health with a unique and efficient service. Visit Pharmamedic.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]