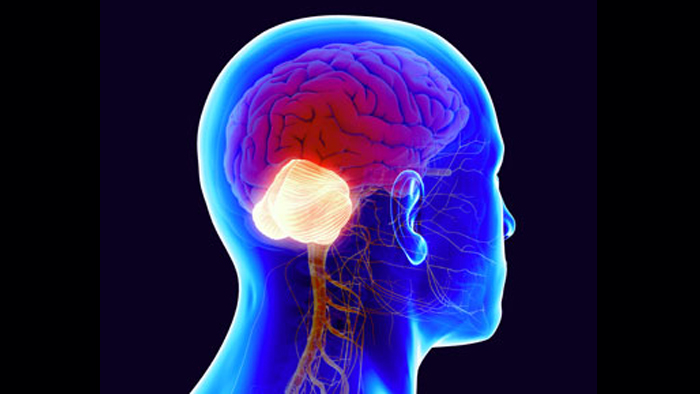
The cerebellum is an oval-shaped structure located in a region of the brain, specifically in the posterior part of the brain, behind the brainstem and below the occipital lobe.
The cerebellum is related to cognitive, language, motor and emotional functions.
The cerebellum is of great importance for the normal or adequate development of the human being, since among its functions is the integration of the sensory and motor pathways. It is linked to the cerebellum with the heartbeat and its frequency. The cerebellum allows the body to move, maintain balance, coordinate eye movements, motor learning, for example, riding a bicycle.
The cerebellum originates from cell bodies of the cerebellar nuclei (nucleocortical fibers) and from a series of nuclei from the pons, medulla, and spinal cord. The cerebellum processes information from other areas of the brain, the spinal cord, and sensory receptors in order to indicate the exact timing for smooth, coordinated movements of the skeletal muscular system.
To make it easier to understand the functions of the cerebellum, imagine it as a kind of coordinator that is in charge of receiving information from the spinal cord and brain structures, to later integrate and control the orders that the cerebral cortex sends to the locomotor system through motor pathways. It is important that patients know each part of their body and what its proper functioning should be, and in the event that you observe different patterns or confusing symptoms, both in you and in your family, do not hesitate to consult a trusted specialist, since they will be able to understand when there is a real need for evaluation.
When we see patients who suffer injuries at the cerebellar level, they are not usually left in a state of total paralysis, but rather with disorders related to the execution of precise movements, maintenance of balance, posture and motor learning.
Likewise, when we see disorders or discrepancies in levels of attention, language processing, music, general learning, and other temporary sensory stimuli, the first thing we would do is explore the cerebellum.
When it comes to pathologies associated with the cerebellum, they usually mention Ataxias, this term does not refer to a particular disease but to a loss of muscle coordination and control in fingers, hands, arms and/or legs. Likewise, we speak of ataxia when there is lack of control of eye movements, all of the above is usually related to neurological problems and probably related to the cerebellum; These abnormalities usually occur when parts of the nervous system that control movement are damaged.
The cerebellum can be cared for if its vulnerability is known. For example, the cerebellum is affected by the excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, the consumption of certain prescription drugs (especially barbiturates and benzodiazepines), heavy metals such as mercury and lead, or solvents such as those used in paint. These elements damage the nerve cells of the cerebellum, which leads to ataxia. Treatment and recovery depend on the toxin involved and the damage to the brain.
The diagnosis of cerebellar disorders is clinical and includes a careful study of the family history and the search for systemic acquired disorders.
Neuroimaging studies are usually performed. When the family history is suggestive, genetic testing is done.
Symptoms of a person who injures the cerebellum:
At the cognitive level, cerebellar lesions can be associated with the following: memory loss, learning deficits, language, executive functions, inhibition and cognitive flexibility including planning.
Other very common ones include:
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Fatigue or sleepiness.
- Speech problems.
- Dizziness or loss of balance.
It is important to see a doctor immediately to diagnose the symptoms.
Recommendations to avoid the risk of stroke:
- Quitting smoking or limiting your consumption is highly recommended.
- Regular exercise or physical activity benefits the heart and blood vessels and reduces the risk of stroke,
- Protect the head with the use of helmets (when driving, motorbikes, bicycles, skates, etc., or when practicing extreme sports),
- Wearing seat belts and staying safe at home reduce the risk of brain injury.
The cerebellum is divided into three parts: there are two large transverse fissures that divide the cerebellum into three main lobes: the anterior lobe, the posterior lobe, and the intermediate lobe.
Difference between cerebellum and cerebrum: The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and controls thinking, learning, problem solving, emotions, memory, speaking, reading, writing, and voluntary movements.
The cerebellum: controls fine motor skills, balance, and posture.
http://www.drpablopena.com/el-cerebelo-y-sus-enfermedades-mas-comunes/