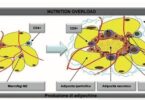
Genetic engineering is a process that uses laboratory technologies to alter the composition of an organism’s DNA.
Genetic engineering allows the genetic code of a cell to be modified to eliminate possible failures in its operation and, incidentally, the diseases that it may cause.
The investigation was in an initial phase, but its authors consider that the technique is very effective. The discovery has been published in the Nature Magazine, one of the most prestigious scientific publications in the world.
Our DNA is encoded through four chemical compounds: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). To describe the DNA of cells, scientists use a very long sequence with these four letters, which are repeated in a specific order.
Genetic editing would make it possible to correct the genetic causes of many diseases: from hereditary blindness to degenerative diseases, or even to modify the genome of embryos so that babies are born free of diseases.
Mutations can result from errors in DNA replication during cell division, exposure to mutagens, or viral infection. Mutations are caused by environmental factors known as mutagens. Types of mutagens include radiation, chemical, and infectious agent. Mutations can be spontaneous in nature.
The DNA of all kinds of living beings can be edited for various purposes: to treat diseases, create transgenic foods, improve non-pathological human characteristics, among other purposes. The manipulation of genes is aimed at understanding their functions and creating disease models. It has been done in many organisms: plants, models like the Drosophila fly, yeast, or zebrafish. And it is a technique that allows precision gene surgery to be performed on human cells. Its function is, deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, encodes the information that cells need to make proteins. A related class of nucleic acids, called ribonucleic acid (RNA) occurs in different molecular forms that serve multiple cellular functions, including protein synthesis.
Genetic engineering This can include a change in a single base pair (A-T or C-G), the deletion of a region of DNA, or the addition of a new segment of DNA.
Genetic alterations have two origins:
Due to external factors, of an environmental nature.
Due to internal factors, of a genetic type.
The following are recommended to improve DNA: a balanced diet,
reduce food toxins and medications, exercise and get away from stress, with all this you can improve your genetic information and thus avoid many diseases.
Variations in non-coding DNA have been linked to various cancers and developmental disorders such as the isolated Pierre Robin sequence. This condition is caused by changes in areas of non-coding DNA that act as enhancer elements. Altered enhancers in the isolated Pierre Robin sequence control the activity of the SOX9 gene.
Many regions of non-coding DNA play a role in controlling gene activity, which is to say that they help determine when and where certain genes are turned on or off.
Changes in DNA can result from errors in DNA replication during cell division, exposure to mutagens, or viral infection. These mutations can increase the risk of cancer or birth defects.
Terms used:
Genetic Engineering: A process that uses laboratory technologies to alter the composition of an organism’s DNA.
DNA: is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all living organisms and some viruses; it is also responsible for hereditary transmission.
Mutation: is a change in the DNA sequence of an organism.
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C3%81cido_desoxirribonucleico