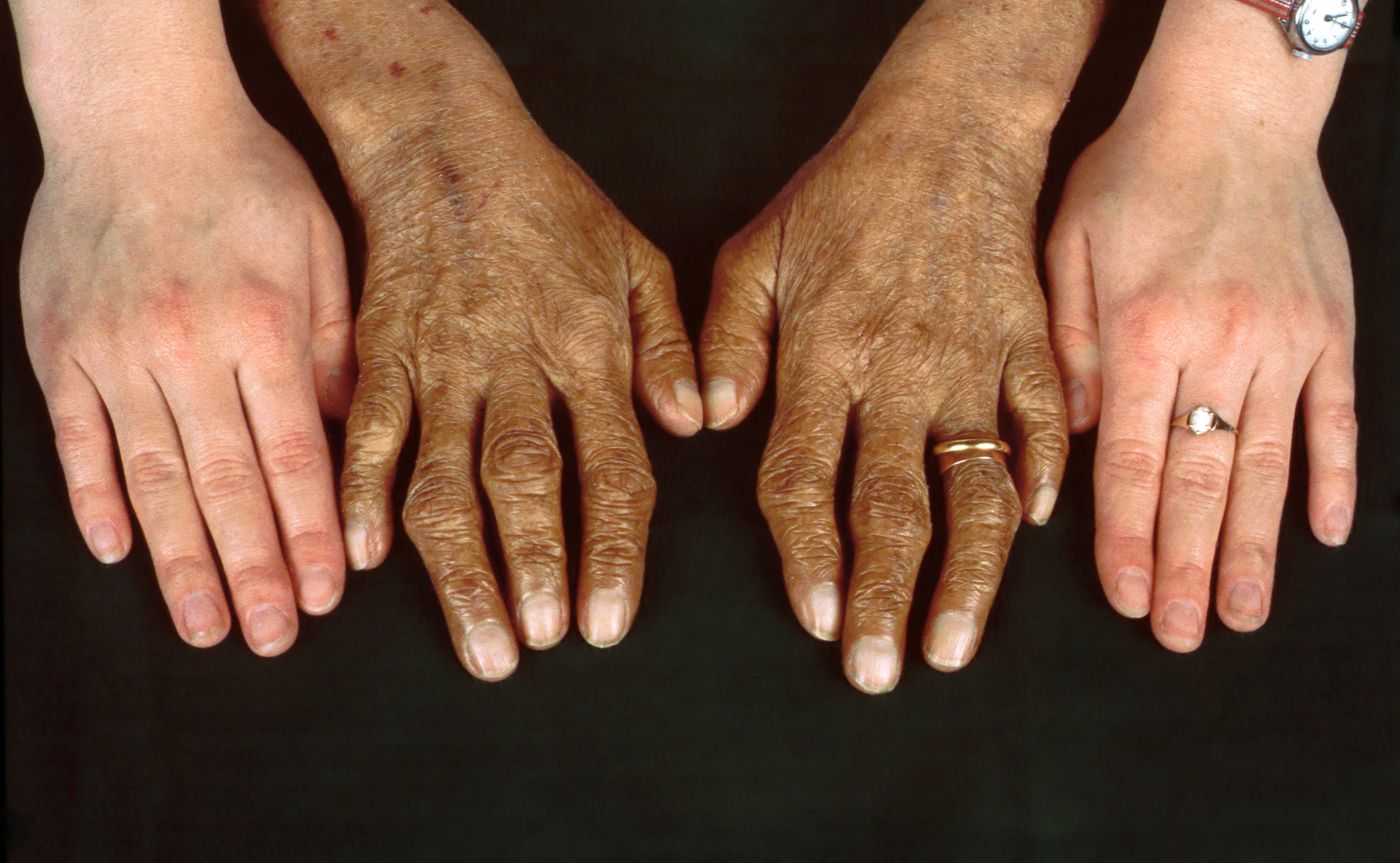
Hemochromatosis is a disorder caused by the alteration of iron metabolism. It is due to an accumulation of iron in the body and, if not diagnosed and treated correctly, can have fatal consequences on the liver, and increase the risk of death from cardiomyopathy. Iron is an essential element for the organism that, in normal physiological concentrations, is found in the body in an amount of around 4 or 5 grams, distributed in hemoglobin, the reticuloendothelial system and the liver, myoglobin, and in various enzymatic systems. However, it is very harmful when it is found in higher amounts, since it generates free radicals that cause organic damage.
It is the most common genetic disease of the white population of the West. It affects one in 200 or 300 people. It is usually suffered by men (in a ratio of five men for each woman), since it is more difficult for iron to accumulate in women due to menstrual losses or pregnancy.
In the evolution of hemochromatosis, different stages can be distinguished:
Stage 1: there is a deficiency but there is still no iron overload.
Stage 2: There is iron overload, but the symptoms are not specific to the disease. The patient presents fatigue and lethargy.
Each patient has different organic damages, depending on where the iron has accumulated in their organism, so they must receive treatment for the different problems that they present.
The goal of treatment of hemochromatosis is the elimination of excess concentrated iron in the organs and treat any organic damage that may have occurred.
The treatment for excessive iron elimination varies depending on the causes of the disease:
Primary hemochromatosis
In the case of primary hemochromatosis, the treatment is phlebotomy, which consists of blood extractions, usually weekly, of about 500 ml each, until the iron level is appropriate. The treatment must be maintained for life, with periodic monitoring of the patient.
Secondary hemochromatosis
In the case of secondary hemochromatosis, the treatment is iron chelators. These are molecules that adhere to iron, forming a soluble substance with it that prevents it from having a toxic effect on the body. The most used chelators are deferoxamine, deferiprone and deferasirox. Tea is also an iron chelator and can be taken with food.
 Maintain an iron level within healthy limits, so it is recommended:
Maintain an iron level within healthy limits, so it is recommended:
Refrain from drinking alcohol.
Limit the consumption of red meat, liver, olives and chocolate.
Avoid raw seafood.
Do not ingest vitamin complexes that contain iron.
Limit the contribution of vitamin C.
Do not take processed or fortified foods.
The use of cooking utensils made of iron should also be avoided.
It is convenient that those people in whose family there is a case of hemochromatosis are carried out tests of early detection of the disease so that, in case of suffering, it can be diagnosed early and start the treatment before any damage occurs.
Always take care of your health with a unique and efficient service. Visit Pharmamedic.