Scoliosis is a lateral deviation of more than 10 ° of the spine that causes a curve.
It is a structured deviation, that is, there are anatomical alterations in the spine that are not simply due to a change in posture and that cannot be voluntarily corrected by the patient.
Scoliosis can be classified by its location as it affects the cervical, cervicodorsal, dorsal, thoracolumbar, or lumbar spine. Because of its laterality, scoliosis can be right or left depending on the convexity of the curve and scoliosis can have a single main curve or a double main curve.
Scoliosis affects 3.5% of the general population, especially women, in most cases it appears in childhood, during growth, and tends to worsen with the fastest growing stages. Therefore, early detection is important, in order to establish therapeutic measures that prevent progression.
Scoliosis does not usually hurt. The reasons that lead the patient to a medical consultation may be the presentation of one shoulder higher than another, a prominent and asymmetric scapula, the more pronounced relief of one of the breasts, the perception of irregularities or asymmetries in clothing or detection of anomalous curvatures of the spine in the medical examinations of the schools.
Among the main types of scoliosis we can find:
Idiopathic scoliosis: of unknown cause. It is the most numerous type, since it groups 80% of the cases. The age of maximum incidence is between 10 and 14 years. It is more frequent in women (80%) than in men (20%). Its incidence is higher in the white race (6%) than in the black race (2%). It is classified in:
- Infant if diagnosed before 3 years of age
- Juvenile, if the diagnosis in children between 4 and 10 years
- Adolescent if diagnosed in older than 10 years.
Congenital scoliosis: secondary to malformations of the spine due to inadequate development of the vertebrae before birth.
Neuromuscular scoliosis: associated with a wide variety of neurological or muscular diseases including cerebral palsy, myelomeningocele, spinal muscular atrophy, muscular dystrophies, and so on.
Scoliosis due to other causes: traumatisms, tumors, bone infections, neurofibromatosis, connective tissue diseases.
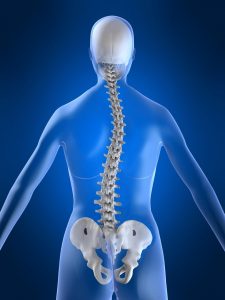 It is classified in different ways according to its cause. Can be:
It is classified in different ways according to its cause. Can be:
- Postural: corrects when the patient lies down.
- Hysterical: it is very infrequent, it has an underlying psychological component.
- Compensatory: caused by discrepancy in the length of the legs.
- Antalgic: is when, for example in a herniated disc, the patient adopts a posture called ‘antalgic posture’ to try to reduce back pain.
- Inflammatory neighborhood, for example appendicitis.
Always take care of your health with a unique and efficient service. Visit Pharmamedic.